Bitcoin was created in 2009 and was invented by an anonymous individual or group of developers known as Satoshi Nakamoto. The emergence of Bitcoin laid the foundation for the development of the cryptocurrency market.
Bitcoin is the world’s first decentralized digital currency or cryptocurrency. It is released as open-source software and is not under the control of any entity.
Bitcoin utilizes a peer-to-peer network, allowing senders to transact directly with recipients without the need for any intermediaries. This eliminates unnecessary fees and makes each transaction much cheaper compared to international money transfer services.
In the world, there is a total of 21,000,000 BTC that will ever be created. No one can change this number, not even the founder, Satoshi Nakamoto. As of January 2023, 19.2 million BTC have been mined, and there are only 1 million BTC left to be mined.
Bitcoin is not only represented by its largest unit, Bitcoin (BTC), but it also has smaller units called Satoshis (or sts), named after the creator of Bitcoin.
With a conversion rate of 1 BTC = 100,000,000 Satoshis, one Satoshi is equal to 0.00000001 BTC.
How does Bitcoin work?
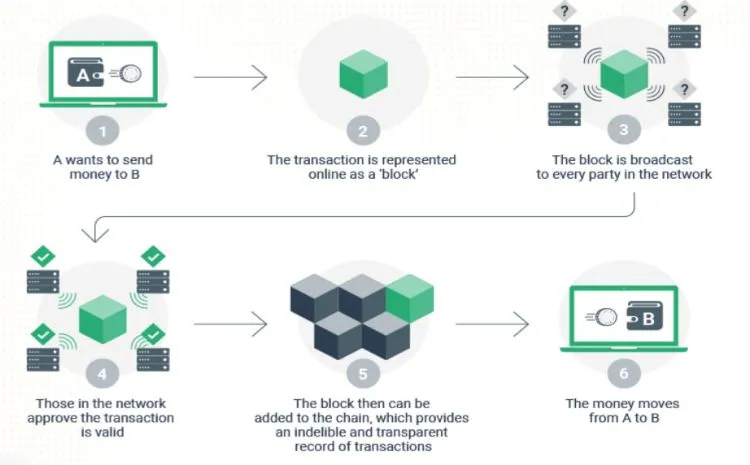
Bitcoin operates based on blockchain technology, a decentralized and public ledger system. Each Bitcoin transaction is attached to a block, and these blocks are interconnected to form a blockchain. The Bitcoin network consists of thousands of nodes (computers) worldwide responsible for verifying and recording transactions.
When a Bitcoin transaction is created, it is broadcasted to the network and awaits confirmation from nodes within the system. These nodes check the validity of the transaction, including verifying the source of Bitcoin funds and validating the electronic signature. Once the transaction is confirmed, it is packaged into a new block and added to the blockchain.
Why was Bitcoin created?
Why did Satoshi Nakamoto create it? The value of Bitcoin depends on each individual and user when they hold, own, or use Bitcoin. Here are some applications:
Bitcoin as a Means of Payment: Bitcoin was created to become a peer-to-peer payment system. Although initially Bitcoin had no intrinsic value, after more than a decade of existence, an increasing number of organizations accept Bitcoin as a means of payment.
Store of Value: Due to its scarcity and the difficulty of mining, Bitcoin is often seen as digital gold. Consequently, Bitcoin is purchased and held by many large financial institutions and individual investors as a long-term store of value.
Borrowing and Mortgage with Bitcoin: In addition to being used for payments, Bitcoin has been accepted by many organizations as collateral for investors to borrow and optimize their capital. Bitcoin is accepted as collateral because it has the highest market capitalization and is the most widely used cryptocurrency.
Conclusion
The birth of Bitcoin initiated the blockchain industry, now valued at billions of dollars. Bitcoin is currently one of the assets that garners significant attention. The high volatility of BTC makes it an enticing investment channel for many, but it also poses significant risks, particularly for novice investors. Having a proper understanding of what Bitcoin is, as well as the cryptocurrency market, is the best way to minimize risks effectively.