What is Polkadot (DOT) vs Cosmos (ATOM)?
Polkadot (DOT)
Polkadot was introduced by Ethereum founder Gavin Wood in 2020. It is considered an improvement of Ethereum. Under the guidance of the Web3 Foundation and developed by Parity Technologies, Polkadot not only operates on a deeper level but also serves as a foundation for other cryptocurrency projects. Polkadot defines itself as a Layer 0 blockchain. Differentiating itself from other Ethereum blockchains such as Solana and Cardano.
Cosmos (ATOM)
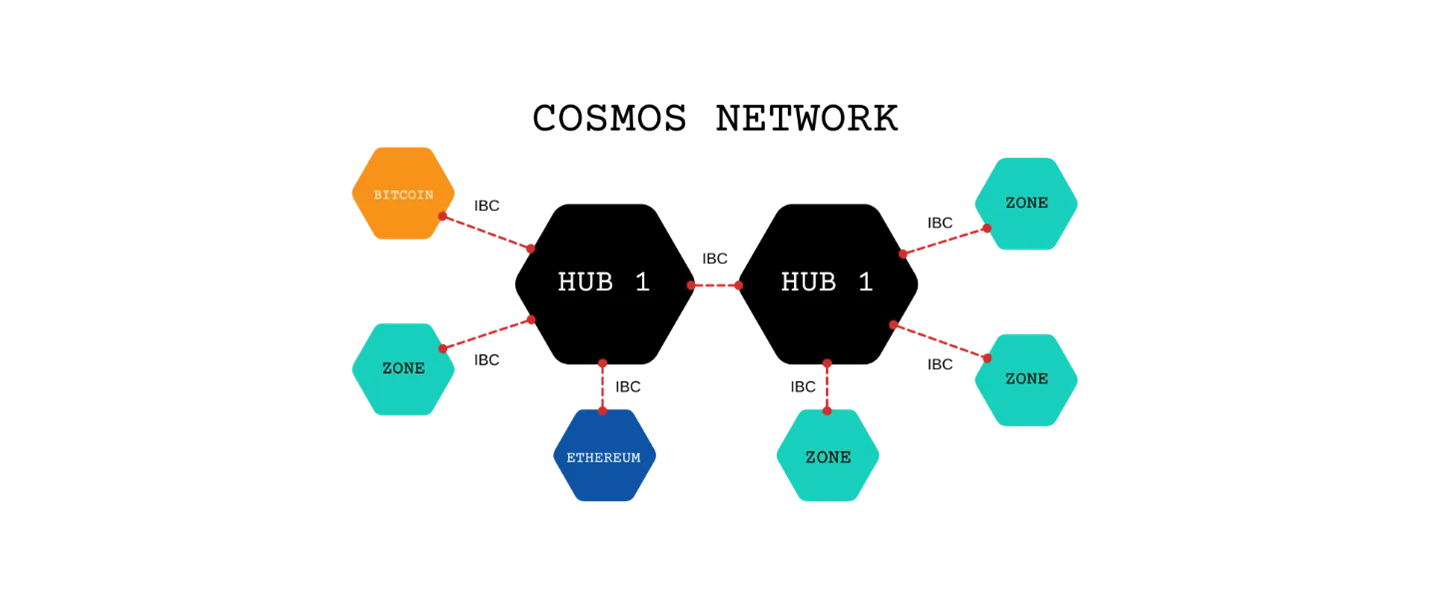
Cosmos was developed by Jae kwon in 2014. Cosmos is known as “The Internet of Blockchains,”. The goal is to create a network that bridges the gap. Enables data exchange between chains without central oversight. Cosmos Hub serves as a central network, connecting chains to interact in a dedicated area. The ATOM token is Cosmos Hub governance.
Cosmos also aims to make it easier for users to create and deploy DApps. By solving the problem of sovereignty in other networks, e.g. Ethereum.
How does Polkadot (DOT) vs Cosmos (ATOM) work?
Polkadot
Polkadot is called a “heterogeneous multi-chain system” because there are three types of blockchains:
• Relay Chain – Main chain that confirms transactions, capable of processing more than 1,000 transactions per second.
• Parachains – Custom chains that use relay chain resources to confirm transactions.
• Bridges – Connect Polkadot with other blockchains.
The layer 0 blockchain is the integration platform, while the layer 1 blockchain empowers the deployment of DApps and NFTs. Polkadot helps programmers focus on optimizing their projects, looking like the “Internet of Blockchains” because it allows blockchains to interact.
Cosmos
When talking about Cosmos, the most important are three main classes:
• Application Layer: The top layer of the blockchain software defines the state and state transition functions.
• Hub and Network Connection: Where blockchains communicate to facilitate transactions.
• Consensus: Handles network agreement, with Proof-of-Stake governed by the Tendermint Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) engine at the core of Cosmos.
By combining all the layers, the developer can easily build the application. This can only be achieved with tools like Tendermint BFT, which makes the Cosmos Hub network robust.
The network achieves consensus between blockchains through the IBC protocol, using the Tendermint BFT algorithm. The individual blockchains communicate through the Ignite CLI using the Application Blockchain Interface (ABCI). Helps developers build DApps in respective networks using multiple programming languages. ABCI is the main bridge between the Ignite CLI and the Cosmos SDK. Helps developers build projects on the Cosmos network. This system interacts and connects with the Cosmos Hub, the main component of the Cosmos network.
Related: Which Is Better Avalanche or Cosmos?
Tokens DOT vs ATOM
DOT
DOT, Polkadot’s native token, aims to combine proof-of-stake authentication, cross-chain interaction, and base layer programming.
DOT can be staked or used as collateral by validators to approve the next block in Polkadot’s blockchain. In this way, DOT acts as Polkadot’s proof-of-stake (PoS) mechanism.
DOT tokens are also used for governance and federation. All DOT holders can vote on network governance, including upgrades and network fees.
ATOM
https://cosmos.network/
ATOM is the underlying governance and utility token of Cosmos Hub. ATOM holders can stake, validate blocks, vote for improvements, and pay transaction fees. Created as a reward for network validators. ATOM’s current circulating supply is 286,370,297 and there is no supply limit. This flexibility is a result of the new ATOM token being created as a reward for stakers. The inflation rate adjusts according to the amount of gold participants deposit.
Polkadot (DOT) vs Cosmos (ATOM)
Polkadot and Cosmos are considered Layer 0 networks with interoperability, allowing Layer 1 blockchains like Ethereum and Bitcoin to run on the same network. The Layer 2 protocol provides improvements such as processing acceleration and scalability.
Although there are similarities, we will now explore the differences.
First, Polkadot provides unified security across the network, with each para-chain backed by an aggregate level of security as the Polkadot Relay Chain. In contrast, connection threads to the Cosmos Hub do not have such a uniform level of security.
Second, Polkadot uses a sharding model for parachains, where changes in one parachain affect all other chains. Cosmos has a hub model, in which multiple hubs are connected in series within regions.
Third, Polkadot transfers tokens and data between blockchains, while Cosmos focuses on transferring assets between blockchains.