What is Polygon (MATIC)?
Polygon (formerly Matic Network) is a blockchain platform designed to address scalability issues without compromising decentralization, optimizing the current developer ecosystem. By expanding and enhancing user experiences, decentralized applications (DApps) are built on the platform to assert its pivotal role within the Ethereum ecosystem.
Essentially, Polygon serves as a Layer 2 scaling solution, utilizing side chains for off-chain computations while ensuring asset security through the Plasma framework and the decentralized Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus network. This ensures the complete security and safety of users. Additionally, the platform is expected to facilitate near-instantaneous transactions with digital assets.
Polygon introduced its first testnet in September 2018, and the latest pre-mainnet version of the network has been successfully deployed. In the future, Matic plans to unveil a user-friendly Plasma wallet, with dedicated WalletConnect support for seamless interaction across various devices. Currently, numerous projects have leveraged the platform’s benefits, with many actively developing applications and integrating with Matic. This IEO project promises to be a hub where developers can deploy and launch decentralized application platforms, thanks to its numerous distinctive features.
Polygon is a Layer-2 solution for Ethereum, developed to address critical issues that Ethereum itself cannot resolve within the current timeframe.
Polygon’s Features (MATIC)
- Scalability: Fast, low-cost, and secure transactions on the Matic sidechain with accuracy mirrored on the main chain and Ethereum as the first compatible layer-1 database.
- High Throughput: Achieves up to 7000 TPS on a single sidechain in the internal testnet. Multiple chains will be added to horizontally scale.
- User Experience: Smooth user experience and developer abstraction from the main chain to Polygon. Support for native mobile apps and SDK with WalletConnect integration.
- Security: Polygon operators also serve as stakers in the PoS system, ensuring security.
- Public Sidechains: Polygon sidechains are inherently public, permissionless, and capable of supporting multiple protocols.
What Problem Does Polygon Solve?
Ethereum, as the largest current blockchain development platform, faces certain limitations that cannot be addressed at present, such as:
- Low Throughput
- Poor UX (excessive gas fees)
- Lack of Sovereignty (shared throughput/ congestion risk, inflexible technology stack, dependence on governance protocols for network improvements, leading to delays)
Many projects use Ethereum-compatible blockchains to mitigate these limitations while still benefiting from Ethereum’s robust ecosystem. However, there is no specialized framework for building such blockchains, and there is no protocol to connect them. This leads to significant development challenges and fragmentation within the ecosystem.
Polygon addresses the aforementioned issues through the following methods:
- Protocol and Framework: Polygon serves as both a protocol and a framework for building and connecting Ethereum-compatible blockchain networks.
- One-Click Deployment: Seamless deployment with just a click for pre-established blockchain networks.
- Developing Custom Networks: Ongoing development of modules to facilitate the creation of customized networks.
- Interactive Protocol: The protocol allows for information exchange with Ethereum and other compatible blockchain networks.
- Security Modules: Options for “security as a service” through dedicated modules.
- Coordinator Modules: Modules that enable interaction capabilities for existing blockchain networks.
How Does Polygon Operate?
Polygon operates through a network of validators who stake their assets to participate in the PoS consensus mechanism on sidechains.
Transaction fees are determined by users on the network, similar to Ethereum. However, with high transaction throughput, transaction fees are expected to be significantly lower than Ethereum due to the market dynamics of gas fees.
In the diagram, the light blue boxes represent sidechains, and the human icons depict the staking layer. Additional sidechains can be added below this staking layer, with multiple darker blue sidechains attached beneath the staking layer.
Basic information about MATIC token
- Token Name: Polygon
- Ticker: MATIC
- Blockchain: Ethereum, Polygon
- Token Standard: ERC-20
- Contract: 0x7d1afa7b718fb893db30a3abc0cfc608aacfebb0
- Token Type: Utility
- Total Supply: 10.000.000.000 MATIC
- Circulating Supply: 6.105.590.937 MATIC
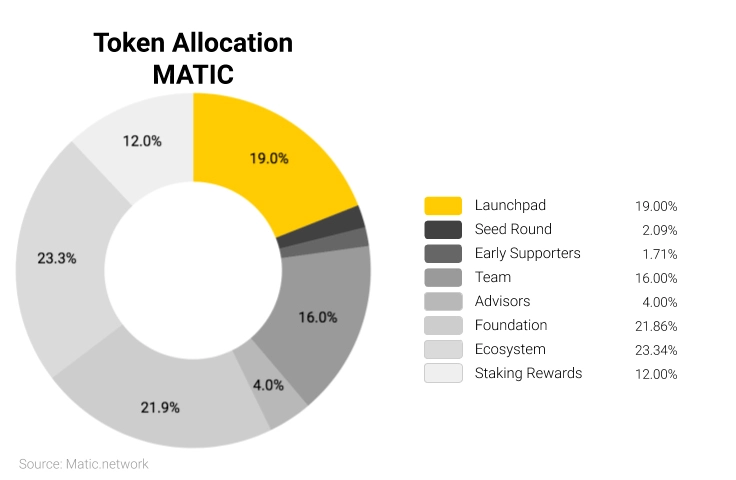
Token Allocation
Token Distribution
- Token Sale: 19%
- Seed Sale: 2.09%
- Early Project Supporters: 1.71%
- Team: 16%
- Advisors: 4%
- Foundation Reserve: 21.86%
- Ecosystem: 23.33%
- Staking Rewards: 12%
Use Cases of MATIC Token
- Payment medium within the network
- Staking
- MATIC token storage in wallets
Storage of MATIC Token
Since MATIC is an ERC20 token, there are several wallet options for storage:
- Exchange wallets
- Common ETH wallets: Metamask, Myetherwallet, Mycrypto,…
- Cold wallets: Ledger, Trezor,…
- Earning and Owning MATIC Token:
- Buy directly on trading platforms.
Related: Polygon Gas Fees Soar 1000% in the Midst of Ordinals-Inspired Token Frenzy
Trading Platforms:
Currently, MATIC is traded on various platforms with a daily volume of up to $2,375,629,742. These platforms include Binance, Coinbase Pro, Huobi Global, OKEx, FTX, Uniswap, Balancer,…
Founding Team:
- Jaynti Kanani (CEO)
- Sandeep Nailwal (COO)
- Anurag Arjun (CPO)
Future and Investment:
Polygon has shown strong growth with the participation of major DeFi projects. Collaborations with partners like Bitmax to establish a low-cost bridge to Polygon are attractive points. The decision to invest in MATIC should be based on thorough research into the project and its prospects for the future.