What is CFD Trading?
CFD trading, short for Contract for Difference trading, is a derivative financial instrument that allows investors to profit based on the difference between the opening and closing prices of a specific asset. CFDs are available on various financial products such as stocks, stock indices, bonds, currencies, commodities, and even cryptocurrencies. One of the advantages is the ability to go long or short, enabling investors to diversify investment strategies and manage risks.
Investing in CFDs also offers leverage, enhancing profit potential. To open and maintain a position, users must provide collateral, known as margin, similar to futures markets. The required margin for trading CFDs is often lower, which is why CFD trading is popular among retail investors.
CFDs on cryptocurrencies involve entering into a contract for the price difference of major cryptocurrencies like BTC, ETH, DOGE, ADA, XRP, and others. For example, the most popular cryptocurrency CFD is the BTC/USD CFD (Bitcoin CFD). The average spread on this asset is 320-450 pips, and the average daily volatility is around 4.5 – 4.6%. This indicates high volatility, exceeding that of major currency pairs by 6–7 times, as well as significantly lower liquidity compared to major currency pairs.
How Does CFD Trading Work?
Now that we understand what a contract for difference is, let’s see how it works. As mentioned earlier, investors do not actually own the asset; instead, they profit from price changes.
For example, when an investor wants to trade CFDs on Bitcoin, they speculate on whether the price of Bitcoin will rise or fall.
Essentially, investors can use CFDs to speculate on the price movement of Bitcoin. Traders can bet on upward or downward movements.
If an investor has bought a CFD on Bitcoin and its price increases, they will sell their CFD. The difference between the buying and selling prices will generate a profit. Profits from these trades are credited to the investor’s account.
Conversely, if an investor believes that the value of Bitcoin will decrease, they can open a short position. To close a position, the investor must buy back the offsetting trade. The net loss difference is then settled in cash through their account.
Related: What is FOMO? 5 Ways to Control FOMO Psychology in the Crypto Market
Example of CFD Trading
CFD trading allows traders to profit from both rising and falling prices. To understand better, let’s look at the following example of trading a Bitcoin CFD:
Assume the current price of Bitcoin is $64,000.
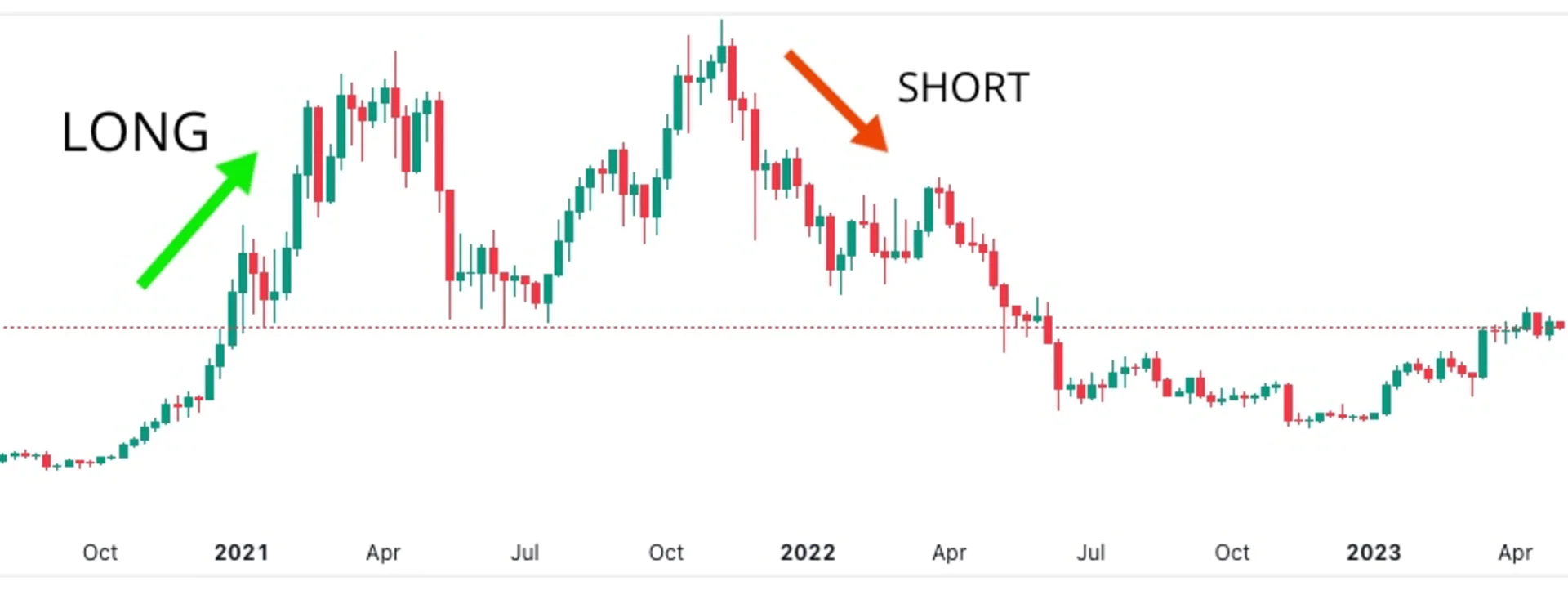
- Short Position: You predict that the price of Bitcoin will decrease, so you decide to open a short position on Bitcoin CFDs. Let’s say the price of Bitcoin drops to $62,000. The difference between the buying and selling price is $2,000. If you decide to short 10 Bitcoin CFD contracts, your profit would be $2,000 * 10 = $20,000.
- Long Position: Conversely, if you believe that the price of Bitcoin will increase, you can open a long position on Bitcoin CFDs. For example, the price of Bitcoin rises to $66,000. The difference between the buying and selling price is $2,000. If you decide to buy 10 Bitcoin CFD contracts, your profit would be $2,000 * 10 = $20,000.
Thus, you can see that whether the price of Bitcoin goes up or down, you can still profit from trading Bitcoin CFDs. The key is to accurately predict the direction of Bitcoin’s price movement and open the appropriate position.
Four Key Components of CFD Trading
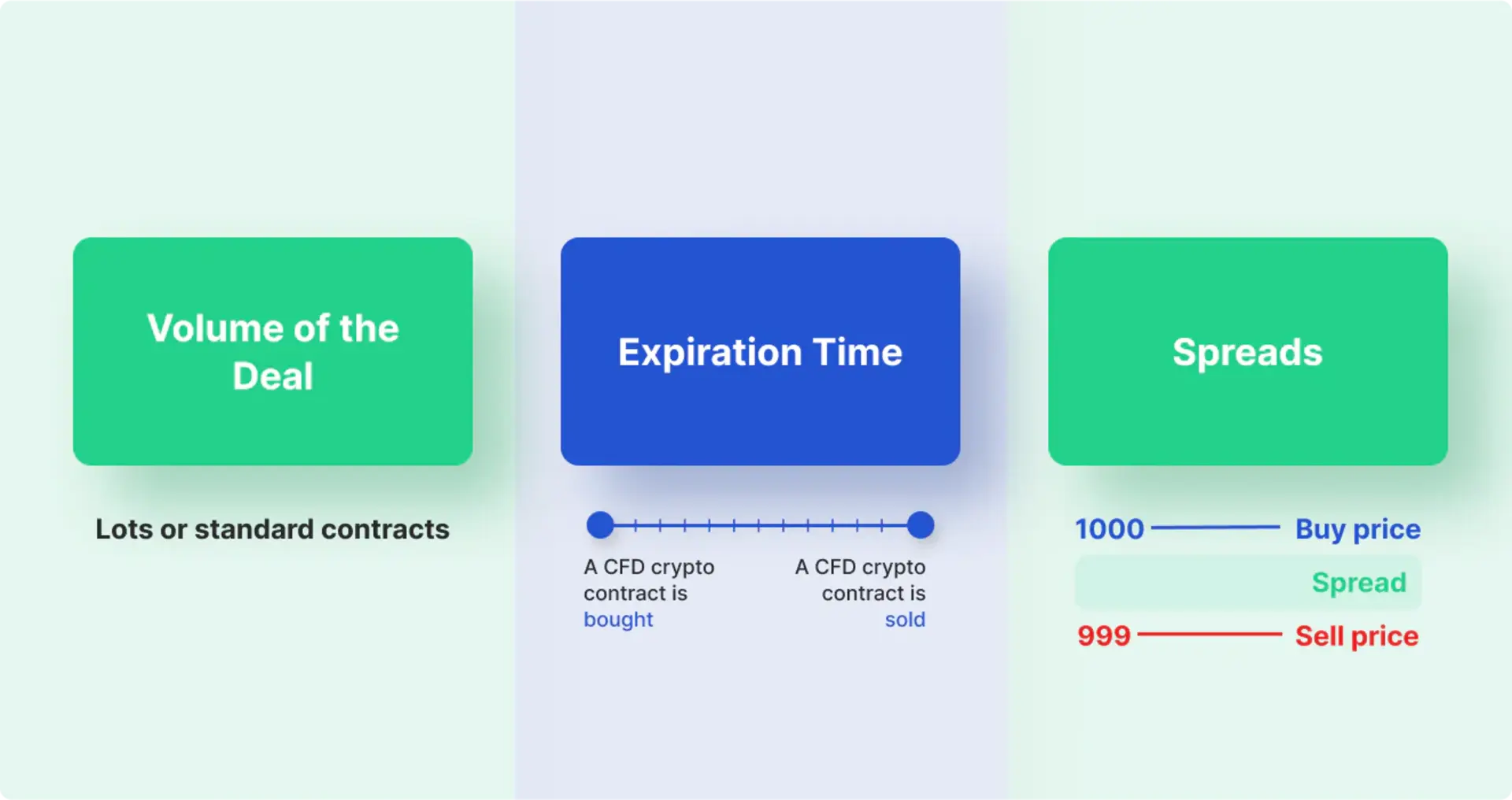
Contract for Difference (CFD) is designed to cater to the needs of all traders, providing enhanced opportunities to trade various contracts. Additionally, cryptocurrency CFD trading has four main components that serve as its foundation:
- Trading Volume: CFDs are traded in lots or standard contracts. The volume of CFDs depends on the specific asset being traded and often mirrors the trading method of the underlying asset. For example, on cryptocurrency exchanges, Bitcoin is traded in whole or decimal portions, and its equivalent CFDs on Forex platforms also mimic the same value in whole or decimal portions.
- Expiration Time: Expiration time refers to the period from when the cryptocurrency CFD contract is purchased until it expires. In most cases, cryptocurrency CFD contracts do not have fixed expiration dates. However, it’s essential to note the exact expiration date of the CFD to ensure that open positions will be automatically closed after the expiration date.
- Spread: Trading cryptocurrencies with CFDs involves using two different price levels: the bid price for opening buy CFD trades and the ask price for opening sell CFD trades. The difference between these two price levels is called the spread, often including the cost of opening CFDs on cryptocurrencies, reflected through adjusted bid/ask prices accordingly.
- Trading Platform: Cryptocurrency CFDs are typically traded through online trading platforms provided by CFD brokers. This allows traders to access the market anytime, anywhere, and manage their positions easily.
Advantages and Disadvantages of CFD Trading
Like any other financial instrument such as options, futures contracts, or spot trading, CFD trading also has its advantages and disadvantages, which we will discuss below.
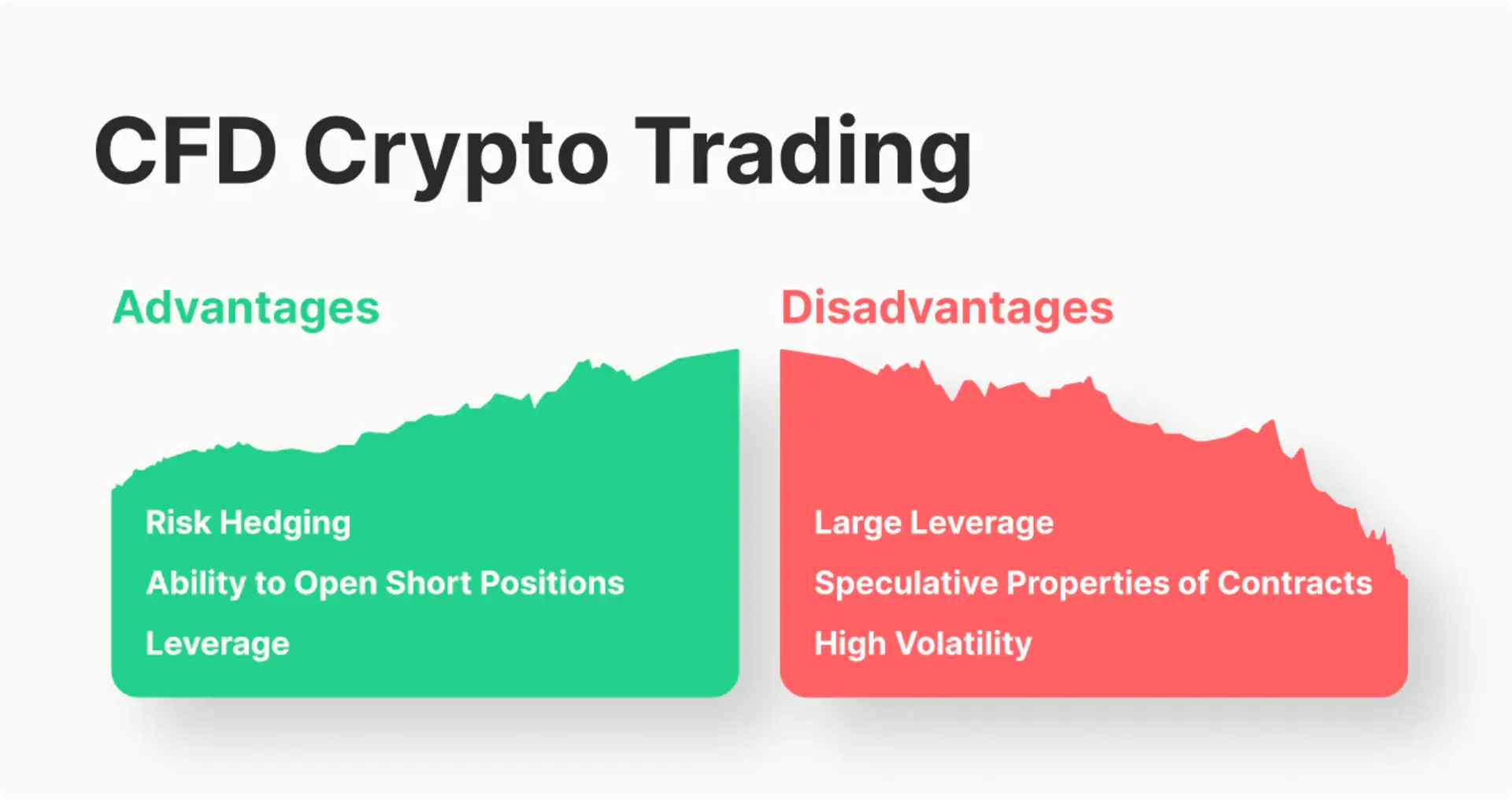
Advantages
- Flexible Risk Hedging: Cryptocurrency CFD trading allows traders to hedge risks flexibly. With this flexibility, traders can open sell CFD positions to offset potential losses. This means that even if a trader owns a large amount of digital assets like Bitcoin or Ethereum and intends to hold them for a long time, they can still protect their profits in the short term if they predict that the prices of these assets will decrease.
- Short Selling Opportunities: CFDs provide traders with the opportunity to profit from the decline in the price of cryptocurrencies. This means that traders can open sell CFD positions to profit when the price of a specific cryptocurrency decreases. This is a significant advantage for those looking to take advantage of market downturns.
- Leverage Utilization: CFD trading allows traders to leverage their positions to increase potential profits. This feature enables traders to develop an optimal trading system, balancing risk and increasing profits that they cannot achieve when using standard spot trading in the cryptocurrency market. However, it’s essential to remember that CFD trading is a high-risk tool and requires careful market analysis before applying it in practice.
Disadvantages
- High Leverage: While leverage trading in cryptocurrencies can yield impressive results, it also carries inherent risks. High leverage increases profit opportunities but also increases the risk of losing deposits. To minimize this risk, traders can use money management principles or reduce leverage levels.
- High Volatility: Cryptocurrency markets often experience high volatility, creating significant opportunities as well as significant risks. This volatility can be unsettling for novice traders and present opportunities for experienced ones. To mitigate the risk associated with using leverage from CFD traders, traders need to carefully adhere to their trading strategies and adjust them as needed.
- Speculative Nature of Contracts: Both futures contracts and cryptocurrency CFDs have speculative characteristics because traders do not actually own the underlying assets being traded. This makes trading unstable and can create unpredictable price fluctuations, especially for beginners.
Overall, CFD trading offers opportunities for profit and risk management, but it’s crucial for traders to understand its intricacies and potential pitfalls before engaging in it.
Trading Both Bull and Bear Markets
Cryptocurrency CFDs are price differential contracts signed for various cryptocurrencies such as BTC, ETH, DOGE, ADA, XRP, and others. For example, BTC/USD CFD is the most common type, characterized by high volatility and lower liquidity compared to major currency pairs.
Differences Between CFDs and Futures Contracts
Cryptocurrency derivative instruments, including options, futures contracts (e.g., Binance Futures), and CFDs, have become some of the most popular leveraged trading methods today. While CFDs and cryptocurrency futures contracts are often considered similar types of instruments, there are significant differences between them:
- Price Origin: In CFD trading, traders determine the price, whereas the price of cryptocurrency futures contracts is determined by cryptocurrency exchanges.
- Trading Fees: CFDs do not charge commissions; instead, trading is based solely on the price difference. In contrast, cryptocurrency futures contracts include both the price difference and the trader’s commission fee.
- Swap Fees: In CFD trading, swap fees are calculated daily, whereas in cryptocurrency futures contracts, the rollover occurs daily within the contract period.
- Brokerage Management: When trading CFDs, the brokerage agency is the counterparty, with the authority to cancel trades and not pay out funds. Conversely, in futures trading, client funds are deposited into a bank account.
- Ownership of Assets: In CFD trading, traders only profit from the price changes of assets without owning them, while in cryptocurrency futures trading, traders become the owners of the assets.
Popular CFD Markets
CFD trading spans across various markets, including:
- Commodities CFDs:
- UK Brent (spot)
- US Crude (spot)
- US Natural Gas (spot)
- Stock Index CFDs:
- GDAX (Dax 30)
- AUS200 (Australia 200)
- ND100m (US Tech 100 – Mini)
- UK100 (UK100)
- SP500m (US SPX 500 – Mini)
- Stock CFDs:
- Amazon
- Alibaba
- Apple
- Microsoft
- American Express
- Cryptocurrency CFDs:
- Bitcoin
- Ethereum
- Litecoin
- Ripple
Risk Management in CFD Trading
As mentioned earlier, CFD trading involves high levels of risk, and to control this risk, you need to use various tools and strategies. Some common risk management techniques include:
- Risk Hedging: Use leverage to short-sell cryptocurrency assets when the market is trending downward.
- Loss Prevention: Hedge against losses by opening hedge positions.
- Stop Loss and Take Profit: Set stop-loss orders to limit potential losses and take profit orders to lock in profits when desired levels are reached.
- Leverage Size: Utilize an appropriate leverage level to balance expected profits and risks.
These techniques help mitigate unfavorable developments due to the chosen trading strategy, especially in a high-risk trading environment like CFDs.
Conclusion
CFDs are a popular derivative trading tool used by experienced investors. While they offer significant opportunities, they also come with high risks. CFD trading has many benefits, such as low margin requirements and easy access to global markets, but careful consideration is needed for factors like leverage and spread.