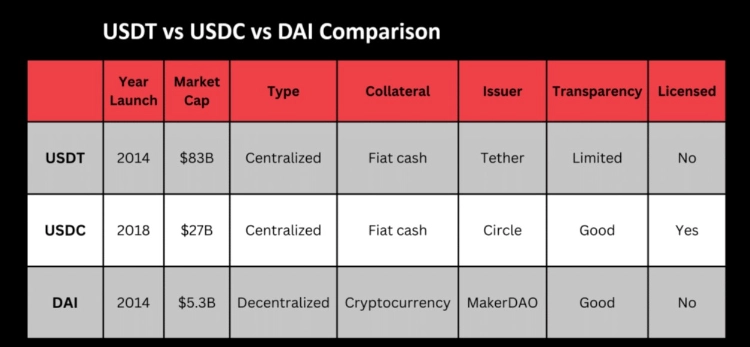
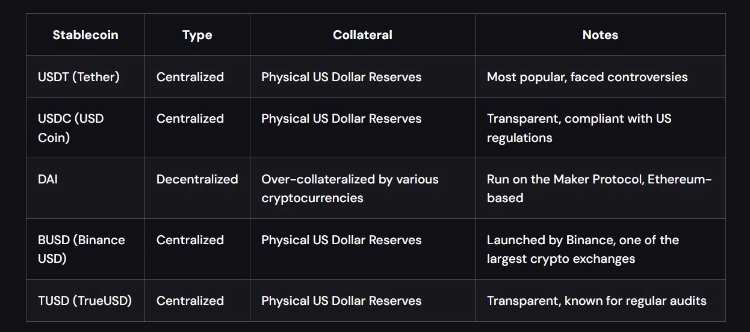
USDT (Tether), USDC (USD Coin), and DAI share a common trait as stablecoins, anchoring their value to the US dollar. USDT and USDC operate as centralized stablecoins, backed by tangible reserves of US Dollars, while DAI takes a decentralized approach, relying on a diverse collateral pool of various cryptocurrencies.
These three stablecoins currently dominate the market, but determining the most suitable option depends on the specific context.
Understanding Stablecoins:
Stablecoins are digital currencies built on blockchain technology, meticulously mirroring the price movements of an underlying asset, typically a fiat currency like the USD. Maintaining a 1:1 ratio with their underlying assets, stablecoins facilitate easy access to traditional financial assets for cryptocurrency holders.
The primary objective of stablecoins is to mitigate the notorious volatility inherent in the crypto market. By combining the stability and liquidity of traditional currencies with the unique features of blockchain, such as decentralization, transparency, security, speed, and programmability, stablecoins provide a practical solution to a persistent challenge in the crypto space.
Purchasing and Usage:
Stablecoins can be acquired on both centralized finance exchanges and decentralized exchanges (DEXs) in the realm of decentralized finance (DeFi) using self-custody wallets.
The Significance of Stablecoins:
Stablecoins play a pivotal role in democratizing access to digital assets, bridging the gap between the crypto realm and traditional finance. They are integral to the growth of decentralized finance (DeFi), a prominent trend in blockchain, forming the foundation for many trading pairs on decentralized exchanges.
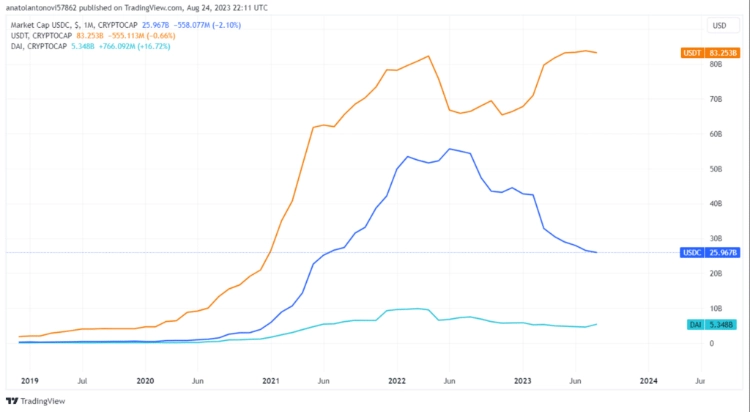
As of mid-August 2023, USDT, USDC, and DAI stand as the top three stablecoins by market capitalization, collectively constituting 10% of the entire crypto market. While Binance USD (BUSD) follows closely, it is not considered in this comparison.
Diverse Approaches to Price Stability:
Although all three tokens strive to maintain a price peg with the US dollar, they employ distinct mechanisms to achieve this goal. Each stablecoin brings its unique features and characteristics to the table, catering to different preferences and requirements within the crypto community.
USDT and USDC function as centralized stablecoins, with centralized entities managing both the token supply and the price-peg mechanism. In contrast, DAI takes a fully decentralized approach, governed by a DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization).
All three tokens rely on collateral, but their mechanisms differ. USDT and USDC are fiat-backed stablecoins, maintaining a 1:1 ratio, while DAI employs an overcollateralized system governed by Ethereum-based algorithms.
Despite utilizing similar methods, USDC is often considered more reliable than USDT due to Circle’s adherence to US regulations and its higher level of transparency. The monthly attestation from Deloitte contributes to USD Coin’s reputation for transparency.
While often referred to as stable ‘coins,’ these cryptocurrencies are technically tokens rather than coins.
USDT vs USDC vs DAI: Which is Best?
The choice depends on the context. USDT, being the most popular option, is widely used, but caution is advised when holding large values due to concerns about its actual reserves and frequent unpegging. USDC, considered a more reliable option, is particularly suitable for business use cases, with Circle offering easily integratable API products.
For those prioritizing absolute decentralization and wishing to avoid centralized entities, DAI stands out as the ideal stablecoin.
About Tether USDT:
USDT, also known as Tether, is a stablecoin issued by Tether Limited, established in 2014. As the oldest major stablecoin, USDT holds the largest market cap, exceeding $83 billion as of August 24, trailing only behind BTC and ETH.
Initially launched on the Bitcoin blockchain using a dedicated software layer called Omni, USDT has since expanded to other chains, including Ethereum, Tron, and EOS. Presently, Ethereum and Tron serve as the primary markets for Tether.
How USDT Works:
USDT operates as a centralized collateralized stablecoin, managed by Tether Limited. In this model, the company holds traditional cash and equivalents in reserves, backing the value of the coin. The process involves minting new USDT tokens when users deposit fiat dollars and burning tokens when users sell them. This mechanism maintains parity between the token’s value and the reserves. However, Tether has faced scrutiny and controversy over the years regarding its claims of full USD backing. The company now provides a ‘Transparency’ page to address concerns.
USD Coin (USDC):
Overview:
USD Coin (USDC) is a significant collateralized dollar stablecoin launched in 2018 by the Centre Consortium, a collaboration between fintech company Circle and crypto exchange Coinbase. Circle serves as the issuer and is responsible for implementing and maintaining the price-pegging mechanism.
Regulation and Transparency:
Circle is registered with the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) and licensed as a money transmitter in various US states, ensuring regulatory compliance. USDC, with a market value of $26 billion, initially launched on Ethereum and later expanded to other chains, including Solana, Avalanche, Algorand, Tron, Stellar, Hedera, Flow, Arbitrum, and Polygon.
How USDC Works:
Similar to USDT, USDC operates as a centralized collateralized stablecoin, maintaining traditional assets in reserves to align with its stablecoin market value. Circle, known for its transparency and reliability, attests USDC reserves through monthly audits conducted by Deloitte, a major accounting firm.
Market Challenges:
Despite its transparency, USDC faced a temporary depegging incident in March 2023, dropping below $0.87 per token due to concerns about Circle’s exposure to the collapsed Silicon Valley Bank (SVB). Government intervention led to a quick recovery. Despite challenges, USDC remains a popular choice for enterprises, offering various business-oriented products suitable for diverse use cases, including payments, payouts, and corporate treasury management.
MakerDAO DAI:
Overview:
DAI stands out as the largest decentralized stablecoin, boasting a market capitalization exceeding $5 billion. Unlike USDT and USDC, DAI operates without central management and is built on the Maker Protocol, a decentralized application (dapp) running on the Ethereum blockchain.
Governance and MakerDAO:
MakerDAO governs the Maker Protocol, functioning as a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) where users collectively vote on updates and the project’s roadmap. With a total value locked (TVL) surpassing $5 billion, Maker is the second-largest Web3 app in the decentralized finance (DeFi) space.
DAI Token:
Launched in 2014, DAI is an ERC-20 token integral to the Maker ecosystem. It serves as a decentralized monetary system, facilitating lending, borrowing, and transactions within the DeFi landscape.
Operational Mechanism:
In contrast to centralized stablecoins, DAI relies on smart contracts and algorithms to dynamically adjust its token supply based on market conditions. The system employs collateralized debt positions (CDPs) to maintain a stable value. When users deposit supported crypto assets, such as ETH, into a vault, new DAI is minted and issued. Crucially, DAI is overcollateralized, ensuring that the value of locked crypto assets remains higher than the circulating supply of DAI. If the collateral’s value falls below a specified threshold, liquidation may occur to uphold the price peg.
Advantages of Overcollateralization:
The overcollateralization strategy employed by DAI sets it apart from algorithmic stablecoins like Terra USD (UST). This approach helps DAI avoid the fate of rapid depegging experienced by some algorithmic stablecoins, ensuring stability and resilience in the face of market dynamics.
In essence, DAI’s decentralized nature, governed by MakerDAO, and its innovative overcollateralization mechanism contribute to its prominence as a leading decentralized stablecoin within the dynamic DeFi ecosystem.