Ethereum recovered and surpassed $3,500 along with Bitcoin’s rise, suggesting that the pre-halving correction period is over.
The bulls were punished
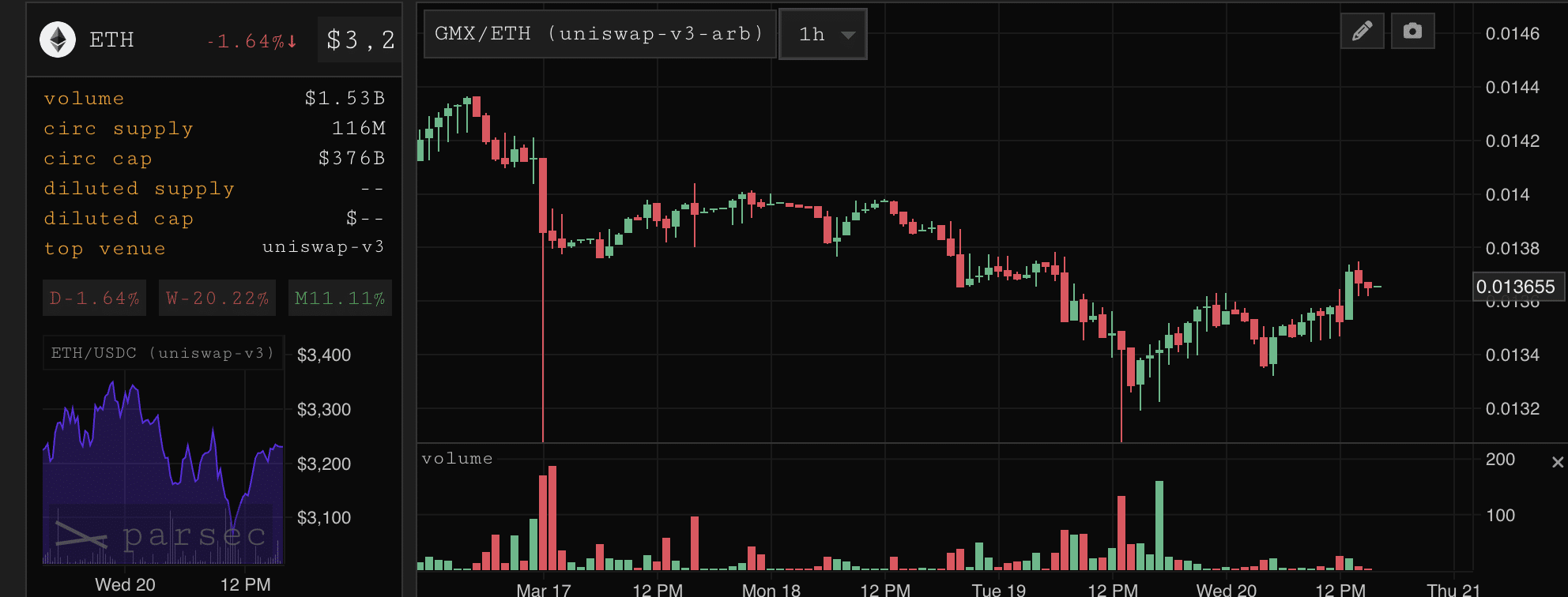
In the DeFi world, according to data from Parsec, there has been more than $5.4 million in collateral liquidated in just the past 24 hours, with $4.27 million related to ETH. If the price of ETH falls below $3008, there could be an additional $24 million in collateral facing the risk of liquidation. On-chain derivatives exchanges such as GMX, Kwenta, and Polynomial triggered liquidations totaling more than $52 million during the same period.
Source: Parsec
The recent increase in collateral liquidation, especially those related to Ethereum, has important implications for the price stability of the cryptocurrency. When a large amount of collateral is liquidated, it could add to the already rising price volatility in the Ethereum market. This volatility could cause a series of sell-offs as assets are liquidated, thereby driving down the price of ETH.
As a result, investors and traders may become more cautious and apprehensive about participating in Ethereum, worried that the price may continue to decline. Additionally, negative sentiment from the apparent liquidation could weaken confidence in ETH, leading to extended periods of price decline.
This volatility, coupled with the possibility of large-scale liquidations, could weaken market sentiment around Ethereum, reducing confidence in the stability and resilience of the platform. Furthermore, the Ethereum network can experience congestion during times of high volatility and increased liquidations, leading to higher transaction fees and slower processing times.
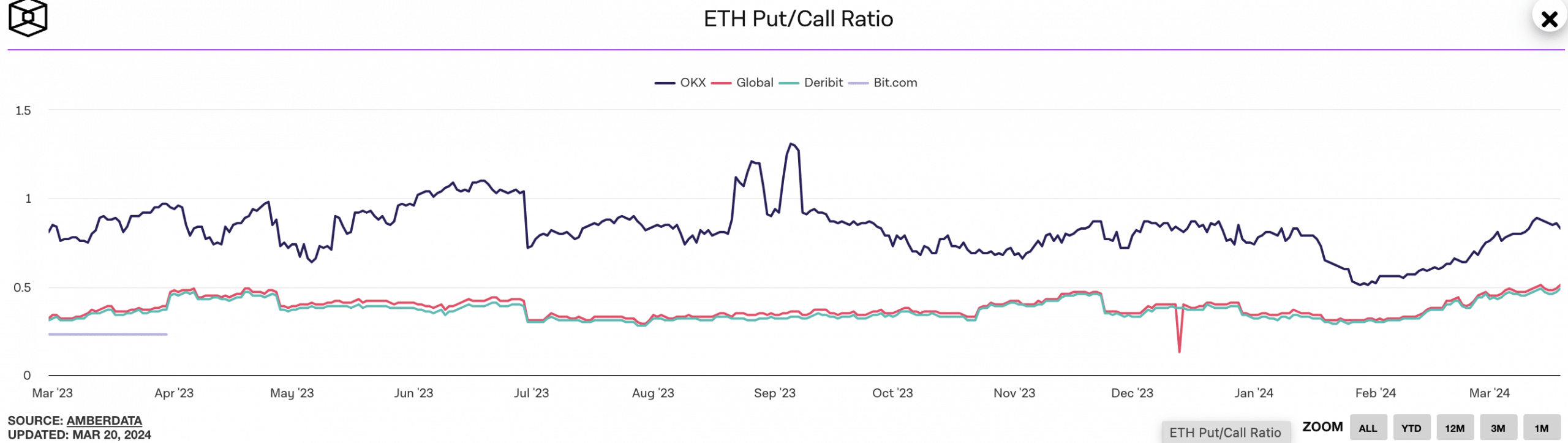
Source: The Block
Congestion can also prevent users from interacting with Ethereum-based applications and decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols, limiting platform growth and adoption. However, the call strike rate for ETH has increased, suggesting that traders are bearish on ETH.
Related: Ethereum Whales Withdrawal Triggers Major Price Decline
More uncertainty
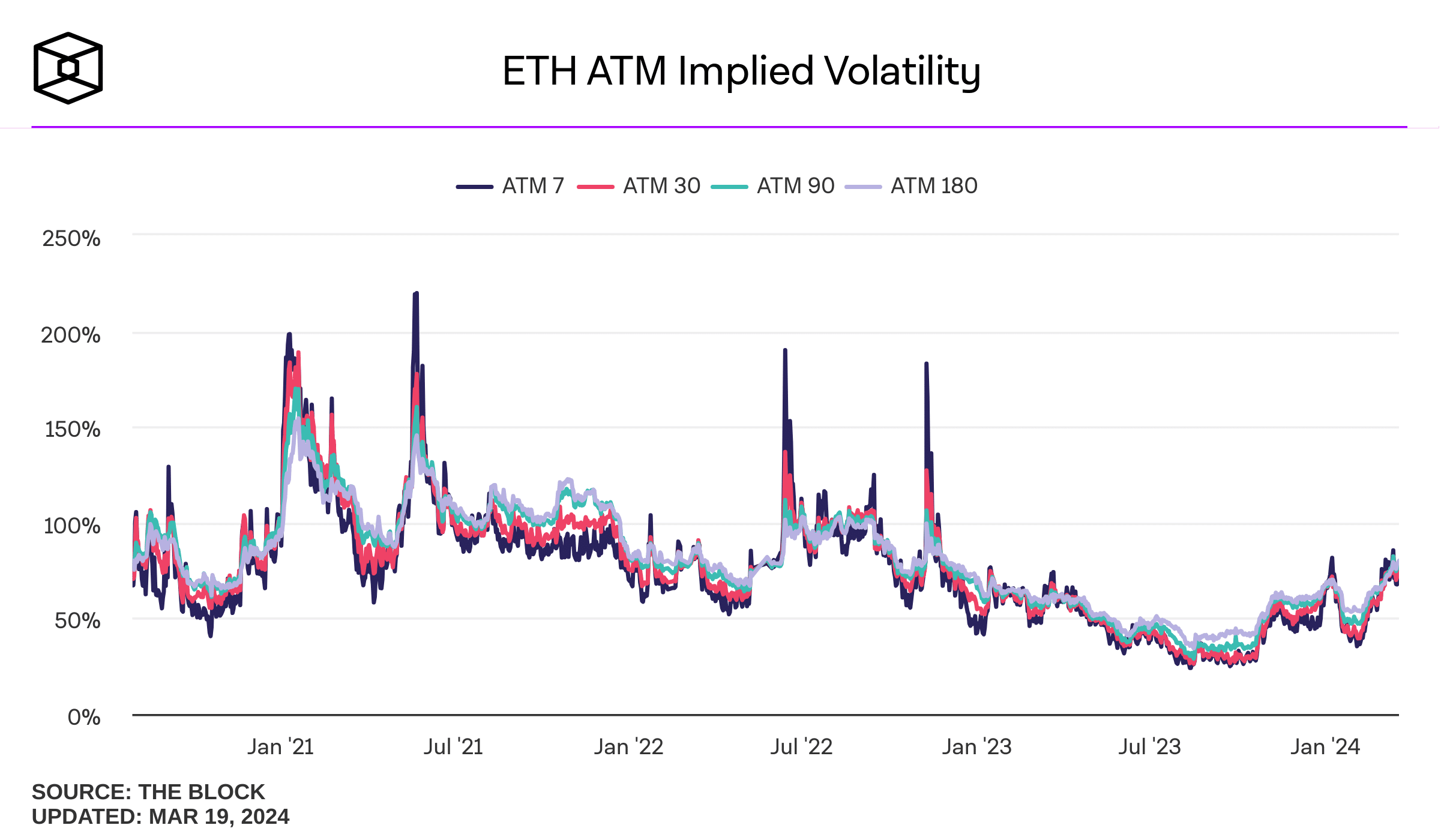
Source: The Block
One of the same reasons is that Implied Volatility (IV) is gradually increasing for ETH. Analysis of ETH data shows that IV has increased significantly.
This signals an increase in price volatility, making it difficult for investors to accurately predict price movements. This can lead to higher transaction costs and increased risks. Furthermore, high IV leads to inflated options premiums, reducing traders’ potential profits.
This could discourage investors from entering or maintaining positions in Ethereum, leading to reduced investor confidence and downward pressure on the price.