The FED plays a crucial role in managing monetary policy and maintaining economic stability. The role of the Chairman of the FED is especially significant, particularly when the FED decides to raise interest rates. So, what is the FED? Let’s explore in detail in this article by AZC.News.
What is the FED?

The FED (Federal Reserve System), also known as the Federal Reserve, is the central bank of the United States, established in 1913 under the Federal Reserve Act. With its essential role in maintaining a flexible, stable, and safe monetary policy for the U.S. economy, the FED operates independently and is not part of the government. It is the only entity in the world with the authority to print U.S. dollars.
The essence of the FED is to create an independent and autonomous financial management structure to maintain the stability of the U.S. economy. The FED’s monetary policy, including setting interest rates and managing the money supply, impacts not only the domestic market but also has significant effects on the global economy. The FED also plays a vital role in providing capital and regulating financial markets during economic crises.
Given its decisive role in the U.S. economy and its significant influence on the global economy, the FED’s decisions on interest rates and money supply are closely watched by both markets and investors.
Why Was the FED Created?
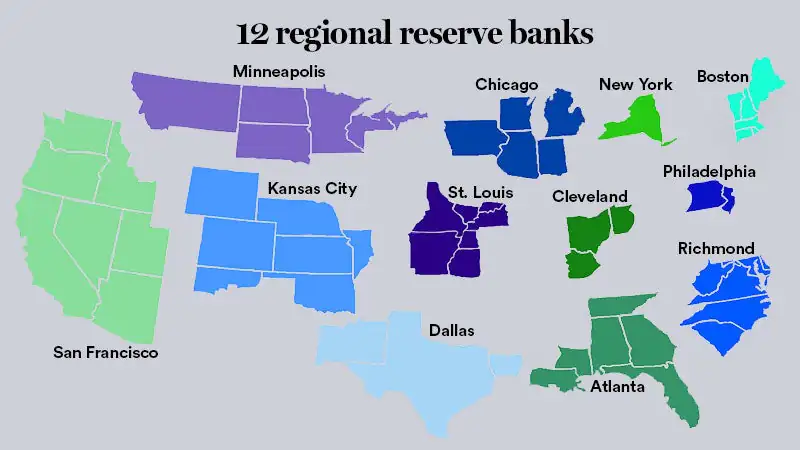
Throughout most of the 19th century, the United States lacked a central bank, leading to numerous financial crises. In 1913, Congress passed the Federal Reserve Act, establishing the Federal Reserve System, which consists of 12 regional public-private banks. The Federal Reserve Bank of New York, responsible for the nation’s financial heart, has long been considered the most important of these. It handles the FED’s transactions, helps manage Wall Street, and oversees one of the largest asset funds.
Related: What is SEC? Information about U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission
The Federal Reserve Districts
Each of the 12 Federal Reserve districts has a central bank, with the Federal Reserve Bank of New York being the largest. The districts are named and identified by number and the city where the central bank is located. Here is a map of the 12 Federal Reserve districts:
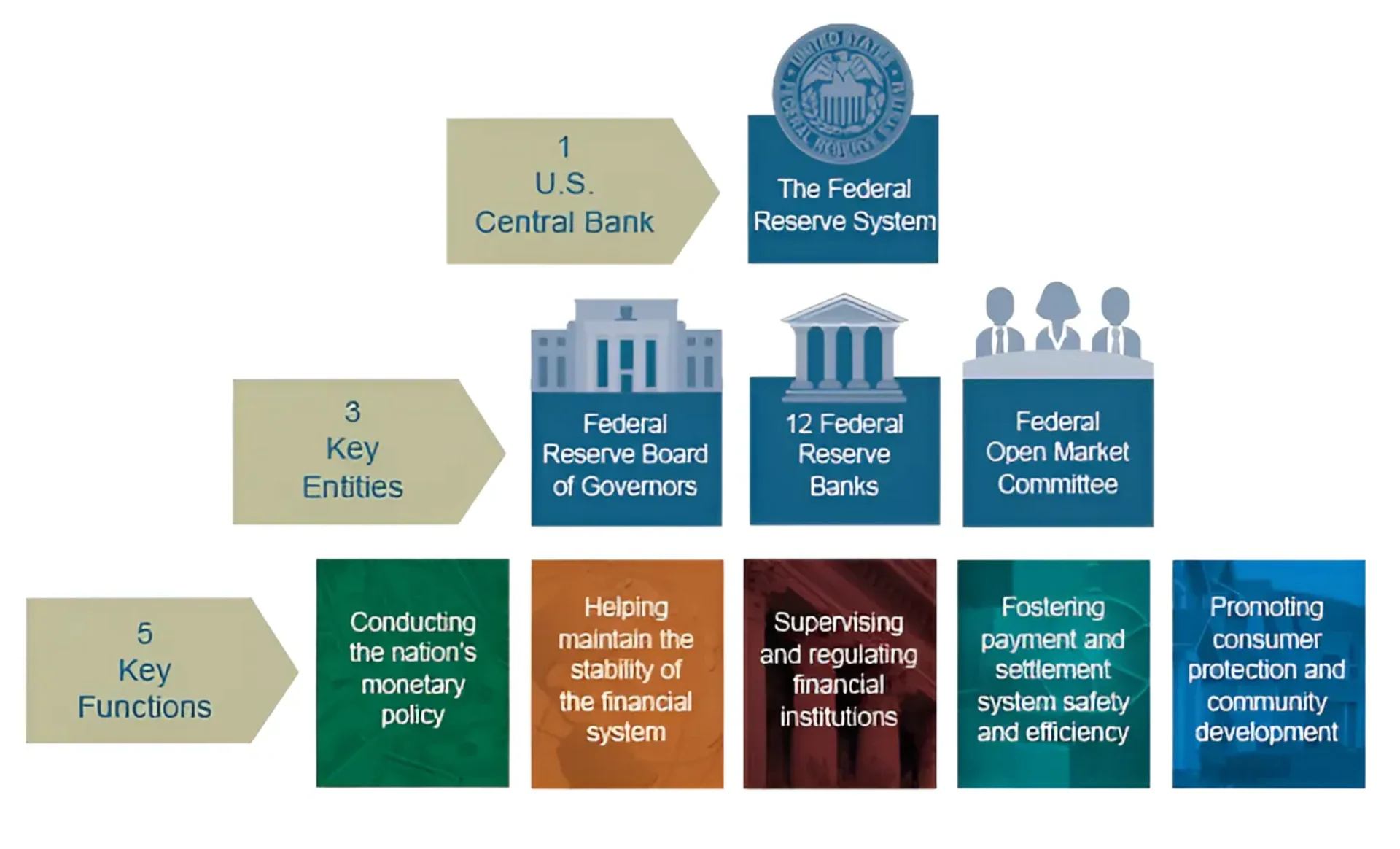
Today, the FED manages U.S. monetary policy, supervises bank holding companies and member banks, and monitors systemic risks in the financial system. The FED’s Board of Governors, with seven members, is the most powerful body, headquartered in Washington, D.C., and led by Chairman Jerome Powell.
Each member of the Board of Governors is appointed by the President for a 14-year term and must be confirmed by the Senate. The Board of Governors is part of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), which includes five regional bank presidents who serve on a rotating basis. The FOMC sets interest rate targets and manages the money supply.
Historically, the FED has had a dual mandate to maintain price stability and achieve full employment. While the FED’s long-standing annual inflation target has been 2%, in August 2020, the FED announced it would allow higher inflation periods to compensate for lower inflation periods. The definition of full employment is debated among economists but is generally understood as an unemployment rate of about 4% or 5%.
To fulfill its mandate, the FED uses its primary tool of buying or selling U.S. Treasury bonds on the open market to influence bank reserves and interest rates. For example, the FED buying bonds injects money into the financial system, reducing borrowing costs. The FED can also lend to commercial banks at a rate it sets (the discount rate) to increase the money supply.
The Role and Responsibilities of the FED in the Financial System
The primary role and responsibilities of the FED are to maintain stability and sustainable growth in the U.S. economy through the management of monetary policy. Specifically, the FED’s roles and responsibilities include:
- Monetary Policy Management: The FED manages monetary policy by deciding on interest rates, controlling the money supply, and promoting price stability.
- Financial System Supervision: The FED monitors and assesses the stability of the financial system, protecting consumers and institutions from financial risks.
- Economic Support: The FED provides central banking services to commercial banks and the government and acts as the lender of last resort in emergencies.
- Market Regulation: The FED intervenes in financial markets to maintain their stability and liquidity.
- Economic Response: The FED evaluates and forecasts economic conditions and implements measures to respond to changes in the economy.
The FED’s role is crucial and impacts not only the U.S. economy but also the global economy. This is because the FED’s decisions on monetary policy can affect interest rates, exchange rates, and global financial conditions.
Who is the Chairman of the FED?
On November 2, 2017, Jerome Powell was officially appointed by President Donald Trump as the Chairman of the Federal Reserve. Before joining the FED, Jerome Powell spent eight years at the Carlyle Group and previously worked in the U.S. Treasury Department under President George H.W. Bush.
Jerome Powell was elected to the position of Chairman of the Federal Reserve in 2018 with 85 votes in favor and 12 against, expected to continue the innovations and advancements in market approaches compared to his predecessor, Janet Yellen. With support from President Donald Trump, known for being a successful businessman, Powell’s decisions were seen as progressive and more aligned with the modern U.S. financial market.
Powell is highly regarded for his vision and market approach, which helps reduce anxiety and create stability in the U.S. economic and financial situation.
The Role of the FED Chairman
The role of the FED Chairman is extremely important in the U.S. financial system. The Chairman of the FED heads the Board of Governors, the body that manages the nation’s monetary policy. In this role, the FED Chairman is responsible for leading and directing the FED’s monetary policy decisions, including setting interest rates and managing the money supply.
Few officials in Washington have as much power and autonomy as the Chairman of the Federal Reserve. They are the spokesperson for the central bank, negotiate with the executive branch and Congress, and control the agenda of the Board of Governors and FOMC meetings. Analysts and investors pay close attention to every statement made by the Chairman, and the market reacts immediately to any signs regarding interest rate policy.
The FED Chairman is appointed by the President, and the FED, an agency that controls its own budget, is largely independent of Congress’s whims. Once confirmed, the FED Chairman is typically not controlled by the White House; there is no accepted mechanism for a President to fire them, and legally, it is not easy to do so.
What is the FED Interest Rate and How Does It Affect You?
The FED interest rate, or Federal Funds Rate, is the interest rate at which commercial banks in the U.S. lend to each other overnight to meet the Federal Reserve’s reserve requirements. It is the most important monetary policy tool used by the FED to steer the U.S. economy and influence the global economy.
The Role of the FED Interest Rate
- Inflation Control: When inflation rises, the FED may increase interest rates to reduce the amount of money circulating in the economy, thereby curbing price increases.
- Economic Growth Promotion: The FED can adjust interest rates to stimulate or restrain investment and spending, guiding the economy towards set goals.
- Financial System Stability: The FED uses interest rates to ensure the smooth operation of the banking system, limiting the occurrence of financial crises.
Impact of the FED Interest Rate
- Exchange Rates: Higher FED interest rates strengthen the USD against other currencies, impacting import/export activities and international investment.
- Domestic Interest Rates: Domestic interest rates may increase following the global interest rate trend.
Who Decides the Interest Rate?
The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) decides whether to raise, lower, or maintain the Federal Funds Rate during its meetings. There are eight meetings each year, and at each meeting, the FOMC discusses the current and future economic situation and provides the rationale for changing interest rates.
What is the Current FED Interest Rate?
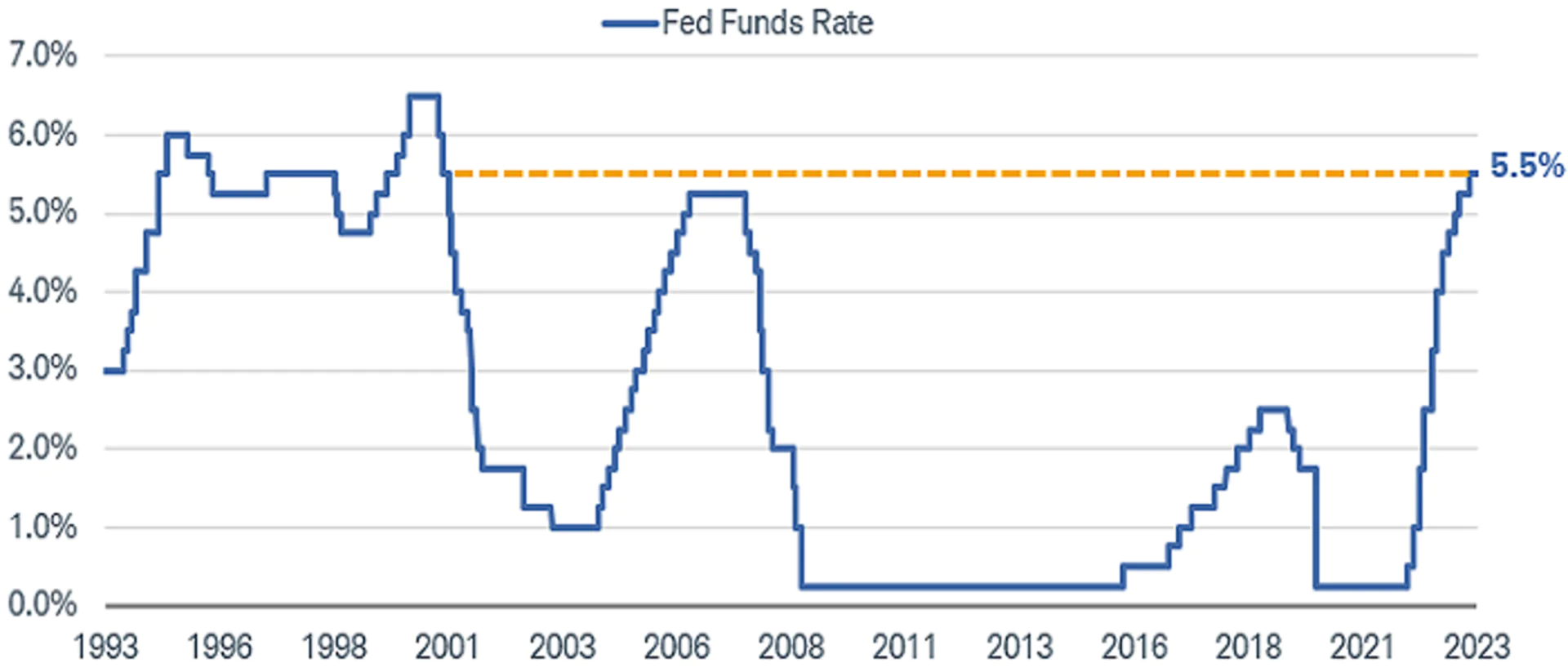
The current Federal Funds Rate is 5.25% – 5.5%, the highest level in 23 years, maintained since July 2023. This interest rate level can affect the global economy in various ways, and experts have different opinions on its potential impact.
Why Does the FED Raise Interest Rates?
The FED does not engage in actual lending or borrowing between banks; it influences the interest rate at which banks borrow within a specific target range. The FED adjusts the interest rate to impact the amount of interest a bank can earn from the FED and the cost of borrowing from the FED.
Raising the interest rate increases the Federal Funds Rate, making borrowing more expensive, ideally slowing down the economy (and inflation). Lowering the interest rate has the opposite effect, making borrowing cheaper.
How Does the FED Raising Interest Rates Affect You?
- For Borrowers: Banks often adjust interest rates for new loans and some existing loans, such as credit cards, home equity lines of credit, and small business loans. Changes in the FED’s interest rate affect the prime rate that banks apply to their customers, which is the minimum interest rate determined by individual banks for highly creditworthy customers. The FED’s decisions on the prime rate are based on the average interest rate of the 25 largest banks.
- For Savers: Banks may adjust interest rates for regular savings accounts and certificates of deposit (CDs). Raising interest rates can attract more savers, helping banks use more deposits to fund loans. In practice, large banks rarely adjust savings interest rates, while smaller or online-only institutions often do. Online savings accounts with the highest interest rates and the best CD rates can yield over 4% annually, with some even approaching 5%.
Does the FED Regulate Cryptocurrencies?
In early August 2023, the FED announced it would start monitoring the expanding activities of the banks it supervises through a new oversight program focused on enhancing the supervision of bank activities related to blockchain technology, cryptocurrencies, and non-bank technology partnerships. According to the FED’s press release, this new program will become part of the FED’s existing oversight activities, with “program specialists working alongside current supervisory teams to monitor banks engaging in novel activities.”
The Impact of FED Interest Rate Hikes on the Global Economy
- Risk of Recession: Continuous FED interest rate hikes in 2022 and late 2023 have raised concerns about a potential global economic recession. This is because higher interest rates can reduce consumer and investment demand, thus hindering economic growth.
- Yield Curve Convergence: Fluctuations in U.S. Treasury bond yields indicate a trend of yield curve convergence for 2, 3, and 5-year maturities. This could be a warning sign of a potential U.S. economic recession.
- Inflation and Unemployment Pressure: The anticipated increase in interest rates is expected to help control inflation and reduce unemployment rates. However, these impacts may occur slowly and remain unclear.
- Financial Market Volatility: Rising interest rates cause increased financial market volatility, leading to shifts in investment capital flows. Investors may turn to safer investment channels like the USD, putting pressure on the financial markets of other countries.
Conclusion
After exploring what the FED is, we can see that the FED is a highly influential organization that plays a crucial role in maintaining global economic stability and growth. Understanding the FED’s role, functions, and impact is essential for assessing macroeconomic trends and making informed investment and business decisions.












🥰
Neco