What is SEC?
SEC is the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission, an independent federal agency established by the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. The SEC is governed by a five-member commission, appointed by the President of the United States and confirmed by Congress, with one member serving as Chairman.
The primary mission of the SEC is to protect investors, maintain fairness, efficiency, and transparency in the financial markets, while facilitating the proper allocation of investment capital. The SEC is committed to building public trust by providing diverse investment opportunities for individual investors, organizations, listed companies, and other market participants.
History of the SEC
The SEC’s origins stem from the Great Depression of the early 1930s. During this period, many private companies engaged in fraudulent practices and provided misleading information to attract investors, artificially inflating stock values. Lack of transparency in financial reporting, information about profit potential, and the sustainability of businesses became a major challenge for investors.
One notable event during this crisis was “Black Monday” on October 28, 1929, when the U.S. stock market began a severe collapse, leading to the Great Depression, the largest economic downturn in U.S. history. Within hours, investors lost billions of dollars, and millions of Americans lost their jobs.
To address the issues uncovered by Black Monday, the U.S. government began constructing a legal framework to oversee and regulate securities-related activities. Established by the Securities Act of 1933 and the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the SEC officially came into existence in 1934.
The primary goal of the U.S. government in establishing the SEC was to enhance transparency and fairness in the securities market, prevent fraudulent activities, and restore investor confidence. The SEC enacted new regulations requiring companies to publicly disclose detailed financial reports, register new securities, and adhere to stricter disclosure rules.
Internal Structure of the SEC
The SEC operates under a hierarchical organizational structure, combining specialization and efficiency in management. This structure includes various high-quality departments and teams, each contributing to the SEC’s comprehensive mission.
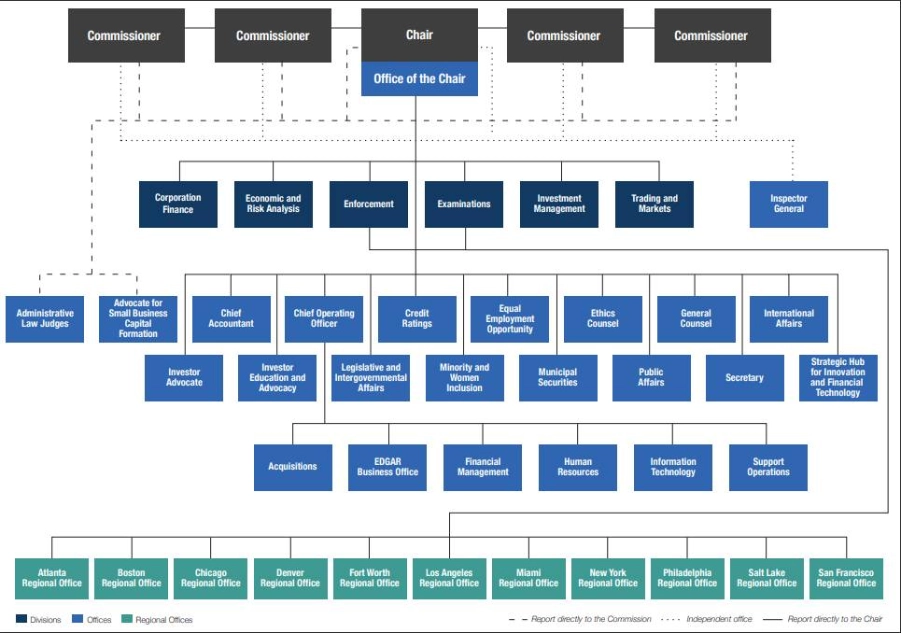
The management structure of the SEC comprises four Commissioners and one Chairman. SEC’s activities are divided into six main divisions:
- Division of Corporate Finance: Evaluates and ensures companies’ compliance with securities regulations.
- Division of Economic and Risk Analysis: Conducts economic and risk analyses to support policy-making.
- Division of Enforcement: Investigates and prosecutes securities law violations.
- Division of Examinations: Examines and evaluates securities organizations to ensure compliance.
- Division of Investment Management: Oversees investment funds and asset management.
- Division of Trading and Markets: Monitors stock exchanges, ensuring fairness and transparency.
This structure is designed to ensure the SEC’s ability to monitor and effectively manage securities-related activities and financial markets while enforcing rules and regulations to protect investors and maintain fairness in the financial system.
Role of the SEC in the Financial Market
The SEC plays crucial roles and responsibilities in overseeing and managing the U.S. securities market, including:
- Protecting investors by requiring companies registered with the SEC to provide transparent information about investment products, minimizing risks for investors.
- Promoting information transparency by requiring listed companies to disclose comprehensive information about their financial status, products, services, management, and business operations.
- Monitoring securities markets, exchanges, investment advisory organizations, brokerage firms, investment funds, and related parties, having the authority to demand information provision and regulatory compliance.
- Regulating the securities market through registration requirements, approving new securities, bond markets, options, and other complex derivative products.
- Investigating and prosecuting securities law violations such as misinformation, fraud, insider trading, and other fraudulent activities through fines, activity bans, and criminal prosecutions.
- Ensuring safety and stability for the financial system by overseeing securities-related activities, enhancing transparency, and minimizing risks.
- Coordinating with agencies such as the Federal Reserve, the IRS, the Bureau of Labor Statistics, and international financial regulatory bodies.
- Providing investor education and training through guidance materials on regulations, safe and effective investment practices.
- Proposing new regulations to improve monitoring and management of the U.S. securities market, including regulations on investor protection, information disclosure, and new financial products.
Powers of the SEC
The SEC is empowered to enforce supervisory measures and penalties for violations of securities laws and regulations in the United States. Some key enforcement measures that the SEC can apply include:
- Auditing accounting records and financial reports of companies to ensure the legality, accuracy, and transparency of financial information.
- Requiring companies to provide detailed information on financial activities, securities transactions, and governance structures to ensure compliance with current regulations.
- Imposing penalties on violators, including fines, suspension or revocation of operating licenses, and even criminal prosecution of individuals involved in serious cases.
- Issuing injunctions against severe violators of SEC regulations, preventing them from engaging in any activities related to the securities market. The SEC may also require violators to be barred or suspended from holding management or director positions in listed companies.
- Civil monetary penalties and disgorgement of illegal profits: The SEC has the authority to impose civil monetary penalties on violators. The penalties can range from tens of thousands of USD to hundreds of millions of USD, depending on the severity of the violation. Additionally, the SEC may require violators to return all illegally obtained profits from the violation.
SEC & Crypto Market
In recent years, the development of the cryptocurrency market has attracted attention and interaction from the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) – the largest securities regulatory agency in the country. The interaction between the SEC and cryptocurrencies has been diverse and complex.
Early Interactions
Initially, interactions focused on determining whether cryptocurrencies could be classified as securities under U.S. law. The SEC believes that some types of cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, may meet the criteria of securities, where investors invest with the hope of making a profit.
In 2017, the SEC warned that some Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) could violate securities laws, causing waves of concern and price declines in the cryptocurrency community.
New Regulations
In recent years, the SEC has issued new regulations to regulate the cryptocurrency market. For example, in 2021, the SEC issued regulations requiring cryptocurrency companies to provide transparent and accurate information to investors.
The SEC is also collaborating with international financial regulatory agencies to develop a global framework for regulating the cryptocurrency market.
Lawsuits
In 2020, the SEC sued Ripple Labs – the developer of the XRP token – alleging that selling XRP as unregistered securities raised billions of dollars from investors. The lawsuit is still ongoing in court.
In 2022, the SEC won a lawsuit against John DeSalvo – the developer of the Blazar Token. DeSalvo was accused of misleading investors about the legality of the Blazar Token and using their money for personal purposes.
By 2024, the SEC had accepted Bitcoin ETFs.
Interactions between the SEC and cryptocurrencies are expected to continue in the future as the cryptocurrency market continues to develop and mature.
Future of SEC and Crypto
The future of the SEC and cryptocurrencies remains uncertain. Currently, the SEC is working to clarify how to effectively and appropriately regulate the cryptocurrency market. However, it can be seen that the SEC is gradually increasing its interest in the cryptocurrency market and is expected to issue new regulations in the future.
The interactions between the SEC and Crypto have had significant impacts on the market. Specifically:
- Increased transparency: The new regulations of the SEC have helped increase transparency in the cryptocurrency market. Companies issuing cryptocurrencies and cryptocurrency exchanges are now required to provide comprehensive and accurate information to investors.
- Risk reduction: The SEC’s regulations have helped minimize risks for investors.
These indicate the important role of the SEC in protecting the interests of investors in the cryptocurrency market.
Related: What is Cryptocurrency? Ways to Earn Money in Cryptocurrency
Conclusion
The SEC has played an undeniable role in protecting transparency and fairness in the securities market. With diverse tasks and responsibilities, the SEC has contributed to increasing market confidence and reducing risks for investors.
There have been significant achievements that the SEC has achieved in ensuring transparency and fairness in the securities market. However, the agency still faces many challenges and needs to continuously improve its operational effectiveness to meet the increasingly complex requirements of the securities market in the future.
After reading the article “What is SEC? Information about U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission“, do you understand what SEC is or not? If not, please leave a comment below to get your questions answered right away!












Hello Kane from AZC. My concern is: how do I contact in case of abuse by a cryptocurrency that refuses to release the assets purchased during the ICo?
Sungguh bijak pemerintah usa dengan melindungi semua pemegang cripto. Good job SEC
If a newly developed Cripto exchange not allowed USDT withdrawal for quite a long time means, what kind of help investors can get from SEC.