What is Proof of Work?
Proof of Work (PoW) is a consensus algorithm introduced in 1993 by Cynthia Dwork and Moni Naor, but it wasn’t widely used until 1999 when Markus Jakobsson and Ari Juels applied it to an electronic payment system. PoW gained global fame when Satoshi Nakamoto, the founder of Bitcoin, used it in the original design of this groundbreaking cryptocurrency network in 2009.

In PoW, entities called “miners” compete to validate transactions and create new blocks on the blockchain. Successful miners are rewarded, usually with a certain amount of newly created cryptocurrency. This algorithm helps prevent fraudulent behavior such as double-spending by requiring significant computational effort.
The Importance of Proof of Work in Crypto
Since its inception to the present day, the primary purpose of Proof of Work (PoW) has remained the same – ensuring security and integrity for blockchain networks.

PoW plays a crucial role in preventing Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks aimed at congesting the system. This is accomplished by requiring miners to invest a large amount of resources such as computational power and time to solve complex puzzles, making the cost of attacking extremely expensive and infeasible.
Additionally, PoW also ensures fairness in the mining process. The contribution of a miner is not dependent on the amount of cryptocurrency they hold but rather on the computational resources they possess. Miners can participate in solo mining or join a mining pool to leverage the combined computational power of the group, increasing the chance of receiving rewards.
Related: What is Cryptocurrency? Ways to Earn Money in Cryptocurrency
Components of Proof of Work
Miners
Blockchain networks using the PoW mechanism rely on a distributed network of computers called nodes. These nodes play a crucial role in confirming and proposing new transaction blocks to the entire network. In this context, nodes are often referred to as “miners” because they contribute computational power and resources to earn the cryptocurrency rewards of the network.
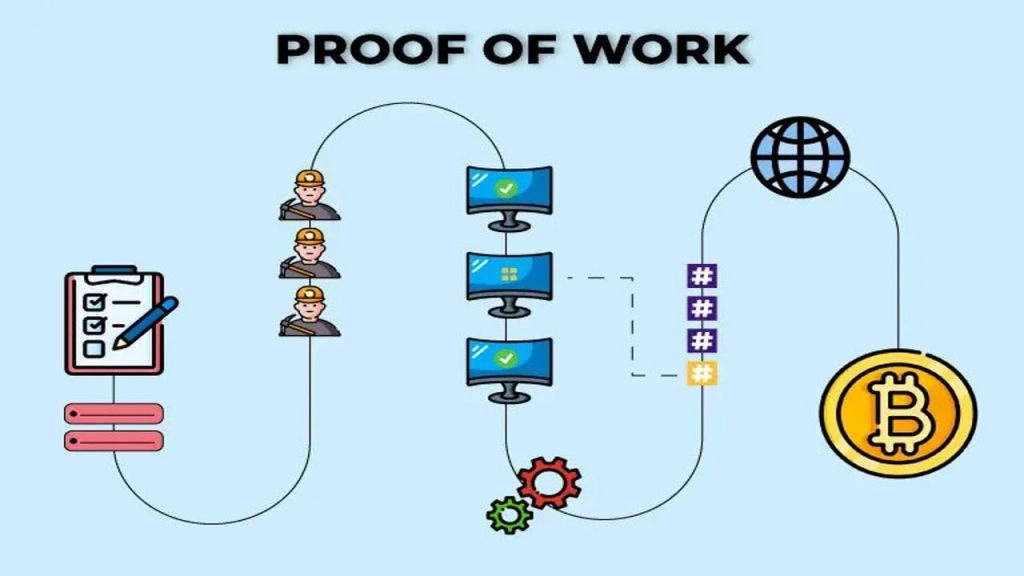
The “Work” in PoW represents the computational power that nodes contribute to confirm a new transaction block. This computational power is demonstrated by solving a complex cryptographic hash function problem, creating a distinctive feature for PoW compared to other consensus mechanisms.
An important difficulty adjustment algorithm ensures that the network takes a fixed amount of time to confirm new transaction blocks. This adjustment occurs approximately every 2016 blocks (about 2 weeks) to maintain a stable block creation time of 10 minutes. Notably, the joining or leaving of miners from the network does not directly affect the difficulty level in short time intervals.
Block Reward
Miners receive a reward when they find a hash value below the threshold set by the network. Upon discovering a valid block hash value, miners broadcast this information to other miners for confirmation and quick integration into their blockchain copy. This confirmation process prevents fraudulent behaviors such as double-spending.
Currently, miners receive a fixed reward of 6.25 BTC per block, along with transaction fees paid by users. This reward mechanism incentivizes miners to competitively participate in the PoW system, encouraging honesty, as any attempt to tamper with the system would result in a waste of resources.
This reward amount halves every 210,000 blocks (about 4 years). This reduction, known as halving, raises concerns about the diminishing incentives for miners if the price of Bitcoin is not high enough. However, as miners leave the network, the difficulty level also adjusts, thereby reducing the cost of mining Bitcoin.
The economics of Bitcoin mining are complex, with many financial factors at play, ensuring that miners continue to operate even without clear profitability.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Proof of Work

Advantages
- High security: PoW protects the blockchain network by making attacks extremely costly in terms of computation power and energy, due to the requirement of massive computational strength.
- Decentralization: No single entity controls the network; anyone can participate in the mining process and transaction verification.
- Resistance to censorship: Miners have an incentive to verify all valid transactions, preventing transaction censorship.
Disadvantages
- High energy consumption: PoW mining consumes a significant amount of energy, negatively impacting the environment.
- Slow transaction speed: Compared to other consensus mechanisms, PoW can lead to slower transaction processing.
- High mining costs: Participating in PoW mining requires significant investment in hardware and energy, resulting in high costs.
- Centralization risk: Due to high mining costs, there is a risk that large mining groups may control a significant portion of the mining power, affecting the network’s decentralization.
Differences between PoW and PoS Mechanisms

Proof of Work (PoW)
- Transaction verification by a network of miners.
- Miners receive rewards in coins and transaction fees.
- High competition for computational power and energy.
Proof of Stake (PoS)
- Transaction verification by validators (staking token holders).
- Validators receive rewards for staking and securing the network.
- Lower requirements for computational power and energy.
Cryptocurrencies Using Proof of Work
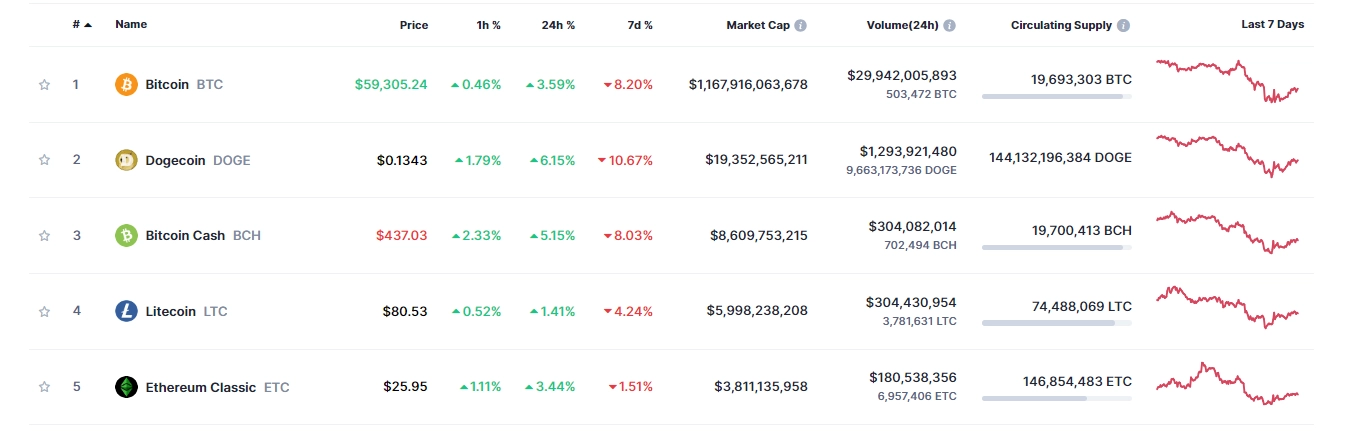
Scoure: CoinmarketCap
Some typical cryptocurrencies using PoW include:
- Bitcoin: The first and most popular cryptocurrency using PoW.
- Dogecoin: Regarded as the largest meme coin in the cryptocurrency market, Dogecoin uses PoW for transaction verification.
- Bitcoin Cash: Similar to Litecoin, Bitcoin Cash is a fork of Bitcoin and uses the PoW mechanism for transaction verification.
- Litecoin: Described as a “lighter” version of Bitcoin, Litecoin operates based on the PoW algorithm.
- Ethereum Classic: A fork of Ethereum, Ethereum Classic maintains the PoW mechanism and has no intention of transitioning to PoS, unlike Ethereum.
Conclusion
Proof of Work (PoW) is a significant consensus mechanism in blockchain, requiring computational power to validate transactions and create new blocks. Miners engage in solving complex cryptographic puzzles and are rewarded with tokens upon success. This differs from Proof of Stake (PoS), where validation depends on the number of tokens users own and have locked.
PoW serves as an incentive mechanism for miners, ensuring security and achieving consensus on the state of the blockchain network. It is currently the most popular consensus algorithm, used in large blockchain networks such as Bitcoin, Litecoin, Dogecoin, and more.
Through the article “What is Proof of Work? Understanding the Importance of PoW,” have you understood Proof of Work or not? If not, leave a comment below to get your questions answered right away!







Good job thanks
是个伟大的创举,,精密。