Proof of Stake (PoS) is an important mechanism in blockchain technology, becoming increasingly popular and favored within the blockchain community. In this article, AZC.News will delve deeper into what Proof of Stake is, how it works, its advantages, and how it plays a crucial role in creating an efficient and sustainable PoS blockchain system.
What is Proof of Stake?

Proof of Stake (PoS) is a mechanism in blockchain systems to ensure the security and fairness of the network by determining block validators based on the amount of cryptocurrency they stake or hold in their wallet.
In this model, users can stake a certain amount of their cryptocurrency, often referred to as stake, to participate in the block creation process and confirm transactions on the blockchain. The more cryptocurrency they stake, the higher the likelihood they are selected as validators and receive rewards for creating new blocks.
Unlike Proof of Work (PoW), where miners must solve a series of complex computational puzzles to prove they have expended a large amount of computational energy, PoS does not require significant energy consumption. Instead, it conditions the selection of validators based on the proportion of cryptocurrency they stake. This not only reduces energy consumption but also encourages users to hold cryptocurrencies long-term, enhancing network stability.
However, PoS also presents some challenges such as fair distribution of tokens and the risk of attack if a large amount of cryptocurrency is concentrated in the hands of a few individuals or organizations.
Related: What is Proof of Work? Exploring the Importance of PoW
History of Proof of Stake
Proof of Stake (PoS) was first proposed in 2012 by cryptocurrency developers like Sunny King and Scott Nadal. Although the idea had existed before, it was not widely implemented until Ethereum began implementing PoS through an improvement called Ethereum 2.0. PoS has attracted attention in the blockchain community for its energy-saving capabilities and enhanced security compared to Proof of Work (PoW).
In PoS, instead of using computational power to create and confirm new blocks as in PoW, PoS miners must stake a certain amount of cryptocurrency to have the right to create and confirm transactions. Thus, PoS has become a popular consensus method deployed in various blockchains.
How does Proof of Stake work?
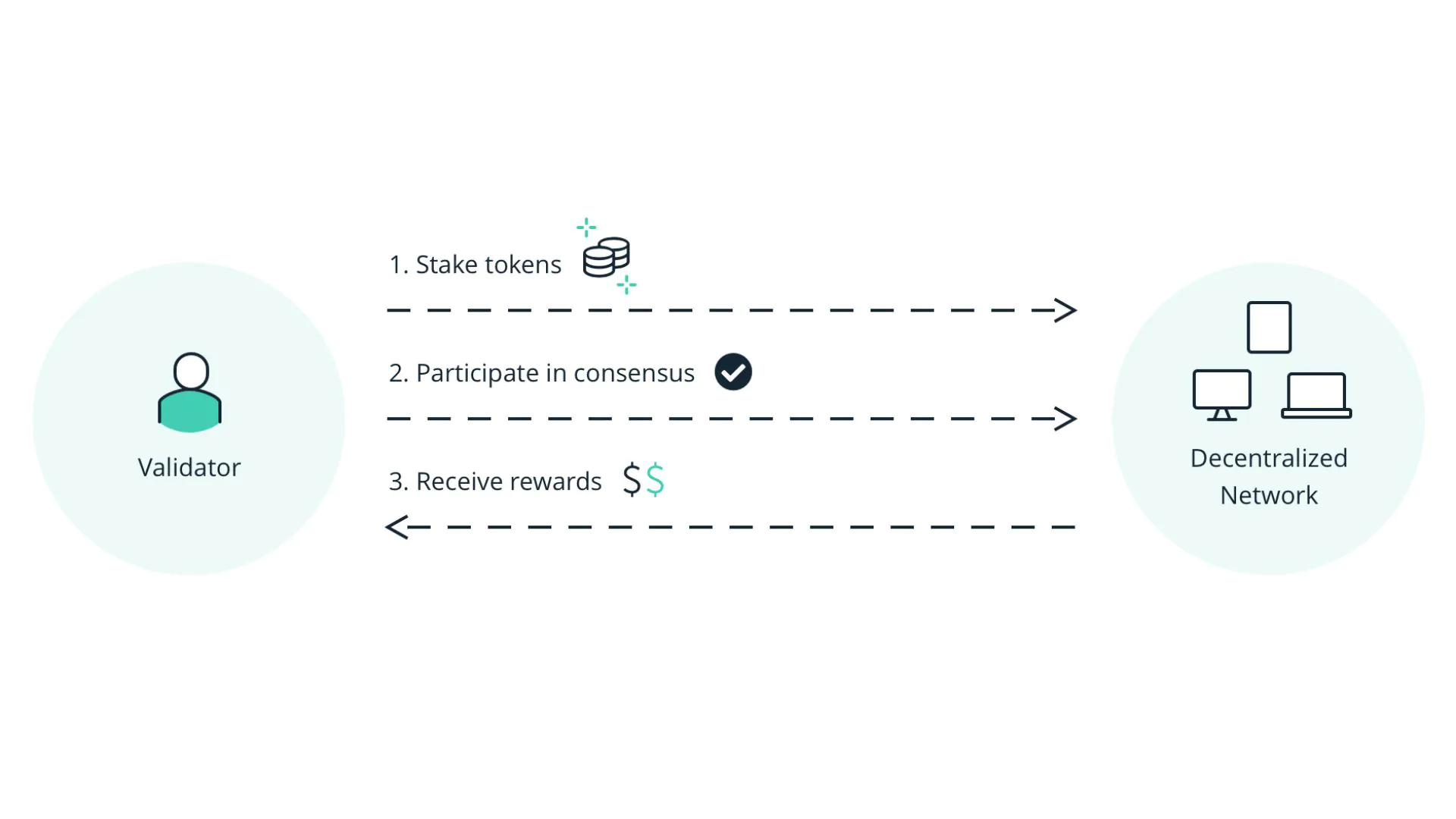
Having understood what Proof of Stake is, PoS operates through the following steps:
- Staking: Users stake a certain amount of their cryptocurrency into the blockchain network. This is often done by sending funds to a specific address on the blockchain or through a specific wallet interface.
- Block Validator Selection: In a specific cycle, the system will automatically select a small number of users to act as block validators based on the amount of cryptocurrency they have staked. The more cryptocurrency staked, the higher the chances of being selected.
- Transaction Confirmation and Block Creation: The selected block validators confirm transactions on the network and create a new block. This process typically involves digitally signing transactions using their private keys to prove that the confirmed transactions are valid.
- Rewards and Penalties: Block validators receive rewards in cryptocurrency for participating in the block creation process. However, if they violate network rules, such as executing invalid transactions, they may be penalized by losing a portion or all of the cryptocurrency they staked.
- Repeat the Process: This process repeats continuously, with users continuing to stake, the network randomly selecting block validators, and block validators confirming transactions and creating new blocks.
This process helps PoS achieve security and fairness in determining block validators while reducing energy consumption compared to Proof of Work (PoW).
Advantages and Disadvantages of Proof of Stake

Advantages
- Energy Efficiency: PoS consumes less energy compared to PoW because it does not require powerful supercomputers to solve complex computational puzzles.
- Enforcement of Security: Block producers in a PoS system have a strong incentive to maintain honesty. If they act incorrectly, they may lose a portion or all of their stake, providing motivation to perform tasks accurately.
- Reduced Risk of 51% Attacks: Compared to PoW, where a user can control over 50% of the entire network and carry out attacks, PoS requires an attacker to control over 50% of the total stake in the network. This is more difficult and costly to achieve.
- Scalability: PoS can easily scale compared to PoW, as it does not require complex equipment and energy for producing new blocks.
Disadvantages
- Potential for Unfair Distribution: Some PoS systems may encounter issues with the fair distribution of initial tokens. Wealthier individuals may have a significant advantage in accumulating more tokens, creating inequality in the network.
- Requires Initial Stake: To participate in block production and earn rewards, users need to have a significant amount of stake. This can create a barrier for newcomers wanting to join the network.
- Vulnerability to Attacks: If an individual or organization owns a large number of tokens, they may have the power to control the network layer and even the entire network, posing issues of honesty and security.
Comparison of Proof of Stake and Proof of Work
Proof of Stake (PoS) and Proof of Work (PoW) are the two most important mechanisms to ensure the security and fairness of blockchain systems. However, they have some differences that make each mechanism unique.
Energy Consumption:
- PoW: Consumes a lot of energy because miners must perform complex computational calculations to prove they have expended a large amount of computational energy.
- PoS: Consumes little or no energy because it does not require complex computational calculations. Instead, the selection of block producers is based on the amount of cryptocurrency they have staked.
Token Distribution:
- PoW: Requires a mechanism to distribute new cryptocurrency into the system, often through rewarding miners when they create new blocks.
- PoS: New cryptocurrency is usually created by rewarding stakers or income from transactions integrated into new blocks.
Decentralization:
- PoW: Can lead to significant centralization of computational power, as miners may concentrate large computational resources in a few physical locations.
- PoS: Can also lead to token centralization, where a large number of cryptocurrencies are concentrated in the hands of a few users or organizations with significant stakes.
Security:
- PoW: Considered one of the safest methods, with security ensured by consuming significant computational energy to attack the network.
- PoS: Also provides a high level of security, but may be easier for attackers if they control a large portion or all of the staked cryptocurrency.
Performance and Scalability:
- PoW: May encounter performance and scalability issues due to increased demand for computational energy as the network expands.
- PoS: Can improve performance and scalability by reducing the need for computational energy.
In summary, both PoW and PoS have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between the two depends on factors such as project goals, the balance between energy consumption and security, and the method of cryptocurrency distribution.
4 Coins Using Proof of Stake Mechanism
- Ethereum 2.0 (ETH): Ethereum, one of the most popular blockchains, is transitioning from Proof of Work to Proof of Stake through Ethereum 2.0. Developers anticipate that this transition will reduce energy consumption and enhance the security and scalability of the network.
Ethereum 2.0 (ETH) - Cardano (ADA): Cardano is a blockchain built on scientific research and uses the Proof of Stake mechanism. It emphasizes security and scalability while providing a decentralized approach for applications and smart contracts.
- Tezos (XTZ): Tezos is a self-amending blockchain based on the Proof of Stake mechanism, where founders can participate in the decision-making process for network development through improvement proposals. It also allows founders to profit from staking tokens.
- Cosmos (ATOM): Cosmos is an interoperable network protocol based on the Proof of Stake mechanism. It allows different blockchains to communicate with each other and share data easily, creating a rich blockchain ecosystem.
Cosmos
Is Proof of Stake Safe?
Proof of Stake (PoS) can be safe or unsafe, depending on the implementation and management of each specific project.
If a PoS project is carefully and securely implemented, token staking will reward users while enabling them to participate in development without needing to know how to code. However, if the project selection is incorrect or if the project is poorly managed or secured, it may lead to significant loss or devaluation of the staked tokens.
Therefore, evaluating the safety of Proof of Stake depends not only on technology but also on the reliability and reputation of the specific project. This sets an important requirement for market participants to research and carefully evaluate before participating in any Proof of Stake project.
How to Mine PoS Coins?
Mining Proof of Stake (PoS) coins differs from Proof of Work (PoW), where miners must solve complex puzzles to “mine” new coins. In PoS, transaction verification and new coin creation are based on the amount of coin you are holding and staking for a certain period.
Here are the basic steps to mine PoS coins:
- Choose a PoS Coin: First, you need to select a PoS coin or blockchain project to participate in.
- Create Your Wallet: You need to create a cryptocurrency wallet to store your PoS coins. Make sure this wallet supports the specific PoS coin you want to mine.
- Purchase PoS Coins: You need to buy a certain amount of the PoS coin you want to mine. This amount will affect the return rate you can receive.
- Transfer Coins to Your Wallet: After purchasing coins, transfer them to your wallet.
- Staking: The process of “mining” in PoS is often called “staking.” You need to stake coins in your wallet as a way to participate in verifying transactions and creating new coins.
- Receive Rewards: Based on the amount of coin you are staking and the time you hold them in your wallet, you will receive new coins as rewards. These rewards are usually distributed at a fixed annual rate.
- Monitor and Withdraw Coins: Monitor your staking rewards and withdraw coins from your wallet when you desire.
Remember that each PoS project may have its own rules for Staking and receiving rewards, so make sure to check the project-specific documentation or information.
Conclusion
The above is all the information about Proof of Stake (PoS). Proof of Stake is not only a transaction verification method but also an important platform for the development and expansion of the blockchain world. With advantages such as energy efficiency, security, and scalability, PoS is becoming a popular choice for many blockchain projects.










Nice project