What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a distributed database system designed to record and store information about digital assets such as cryptocurrencies. These data are organized into blocks, containing transaction history and balance fluctuations. Each block is connected to the next through cryptographic hash functions and arranged in chronological order, forming a chain.
Blockchain is also known as Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) because it does not rely on any single organization or intermediary. The information stored on the blockchain is immutable, tamper-proof, and cannot be deleted unlawfully.
Origin of Blockchain
The concept of blockchain technology was first proposed in the early 1990s by two researchers, Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta. However, it was not until the end of 2008, when Satoshi Nakamoto published a white paper introducing a new peer-to-peer electronic cash system called Bitcoin, that the operational model of blockchain technology was clearly defined and described.
Bitcoin blockchain was launched on January 3, 2009, when the first block was mined by Satoshi Nakamoto, with a block reward of 50 Bitcoins. The first bitcoin transaction in the world took place on January 12, 2009, when Satoshi sent 10 Bitcoins to Hal Finney, a software developer in the United States.
Blockchain technology was created with the aim of addressing limitations in traditional transactions and eliminating issues like double spending and third-party intermediaries such as banks and payment services.
Features of Blockchain
Blockchain possesses the following characteristics:
- Decentralization: Blockchain operates independently without the control of any organization or entity, relying on algorithms and validating nodes to ensure decentralization. This enhances transparency and reduces the potential for fraud.
- Distribution: The blockchain network is maintained by nodes worldwide, distributing computational power across multiple computers to ensure stability.
- Immutability: Data recorded on the blockchain cannot be changed or modified once written into a block, thanks to consensus algorithms and hash functions.
- Security: Blockchain utilizes cryptographic techniques to protect information, encrypting data into hash functions. Each block in the blockchain has its own hash and the hash of the previous block, ensuring data integrity and immutability.
- Transparency: All transaction information on the blockchain is publicly available, allowing anyone to verify and access transaction history.
- Trustlessness: The blockchain network operates based on automated transaction validation by nodes, without the need to trust any single entity. Nodes only need to follow the blockchain algorithm to operate and maintain the network.
Structure of Blockchain
Blockchain consists of “blocks” to form a “chain.” Specifically:
- Block: Contains transaction data on the blockchain.
- Blocks expand over time in terms of quantity and are linked together to form a chain.
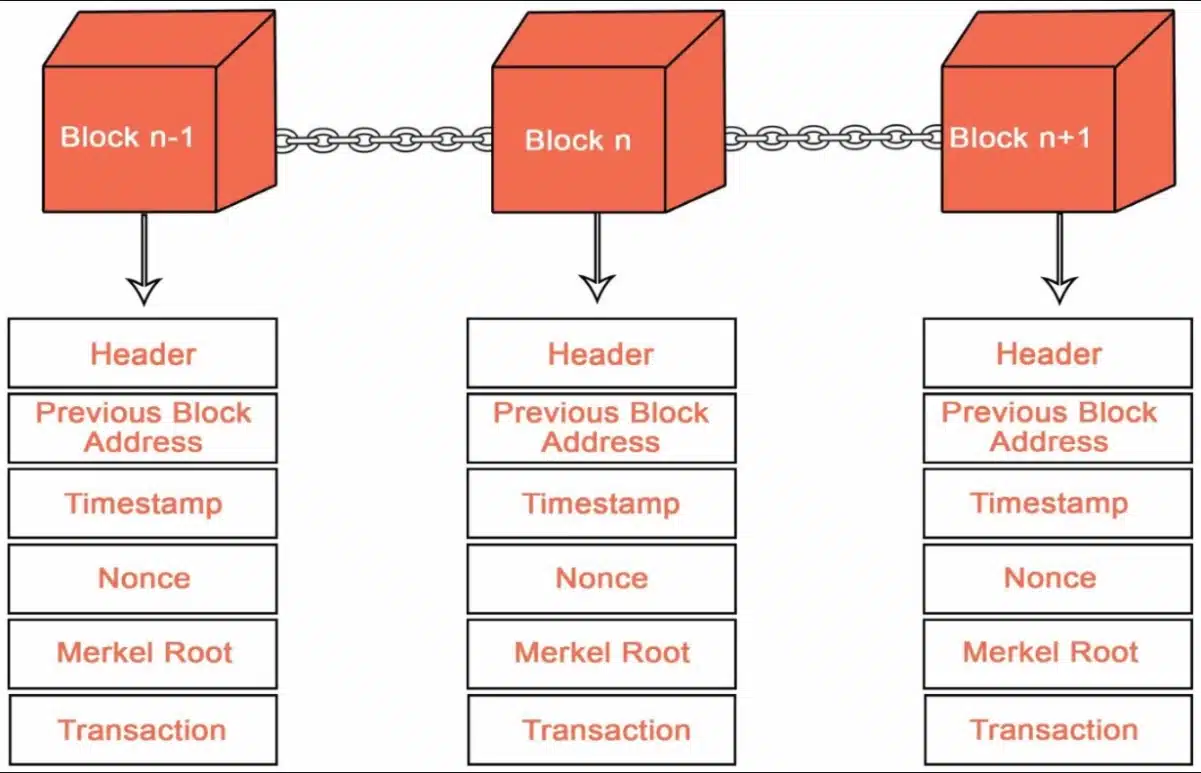
Each block comprises the following components:
- Block Header: A hash function containing information to identify a specific block on the blockchain, including the hash of the previous block, timestamp, nonce, and Merkle root.
- Previous Hash: The hash of the previous block.
- Timestamp: The block’s creation time.
- Nonce: Each block in a blockchain has a unique nonce, calculated during the process of mining, to create a unique hash value for the block.
- Merkle Root: The final hash value of the process of pairing and hashing transactions in the Merkle Tree.
Hash is a string of characters encoded using cryptographic hash function technology from predefined input information.
How Does Blockchain Work?
The process of processing transactions on the blockchain occurs as follows:
Step 1: Users request transaction execution. At this point, transaction information is recorded on the system, creating a record and sending it to nodes for validation.
Step 2: Computers in the system (called nodes) validate the transaction records according to the consensus algorithm on the blockchain.
For example, assume a user needs to execute a transaction of 3 bitcoins:
- Nodes will verify if there are 3 bitcoins in the user’s wallet, and if so, the transaction will be executed.
- If the user’s wallet only contains 1 bitcoin, the node determines that the user’s wallet does not have enough bitcoin to execute the transaction, and the transaction will not be executed.
Step 3: The validated user records are stored in a block.
Step 4: The newly created block is added to the chain by connecting the Previous Hash of the block to be added with the hash of the previous block, forming a blockchain.
The first block has no block before it, so it has a Hash of a string of 0, called the primitive block or Genesis Block.
Blockchain Consensus Mechanism
The consensus mechanism of the blockchain is a mechanism for nodes to follow to ensure that transactions on the blockchain are accurate and consistent across all nodes in the network.
If there is a data change in the network, it will be compared with the data of other blocks to ensure accuracy and consistency with the previous block. If there are differences, the data will not be allowed to be written inside the blockchain. This is how the blockchain is designed to prevent data changes.
For example, if a hacker attacks and changes the information on block n:
- The hash of block n is changed.
- The system will compare the hash of block n with the hash of the previous block to detect discrepancies.
- The hacker must change the hash of the previous block. The system will detect discrepancies in block n-1. The hacker must continue to change the hash of block n-2.
Therefore, to change a transaction, the hacker must change all the blocks to comply with the consensus mechanism of the blockchain.
Consensus mechanisms ensure the accuracy and transparency of the blockchain.
The consensus mechanism is an essential part of a blockchain, playing a core role in keeping blockchains decentralized and secure. Some common consensus mechanisms include:
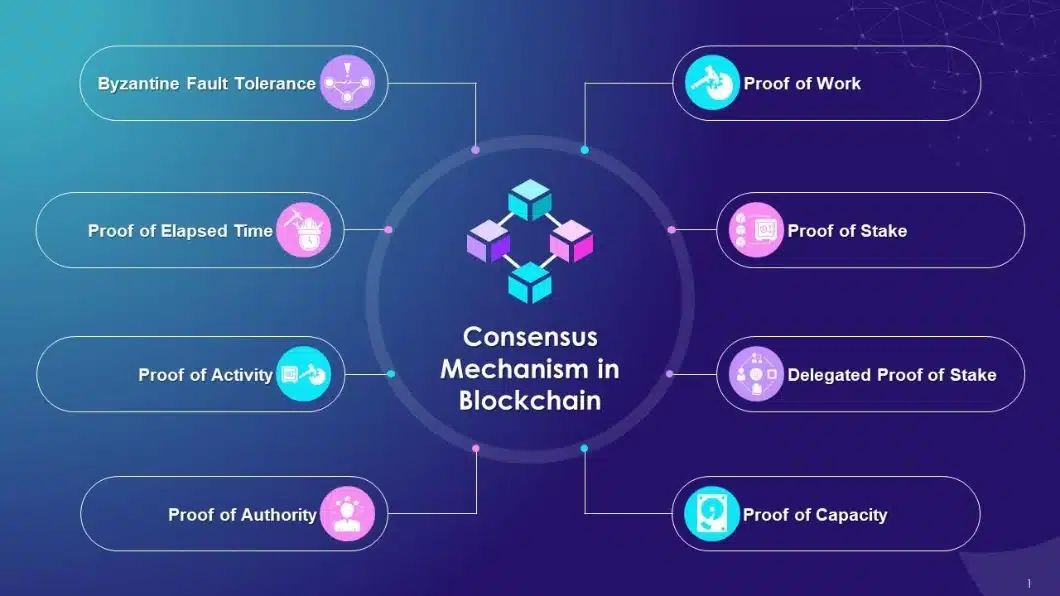
- Proof of Work (PoW): Miners use computer power to solve cryptographic puzzles to create hash values. After solving, they gain the right to validate transactions and create new blocks in the blockchain. Examples: Bitcoin, Ethereum, Litecoin, Monero…
- Proof of Stake (PoS): Users must stake a large amount of coins/tokens to gain the right to become transaction validation nodes and create blocks. Examples: Ethereum 2.0, Polkadot, Algorand…
- Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS): Token holders can vote and delegate nodes to verify transactions. Examples: EOS, Tron, BitShares…
- Proof of Authority (PoA): The algorithm emphasizes the value of identity & reputation of participants rather than relying on the value of the tokens they hold. Examples: MakerDAO, VeChain…
Related: What Is Ethereum (ETH)? An Overview of the ETH Project
History of Blockchain Technology Development
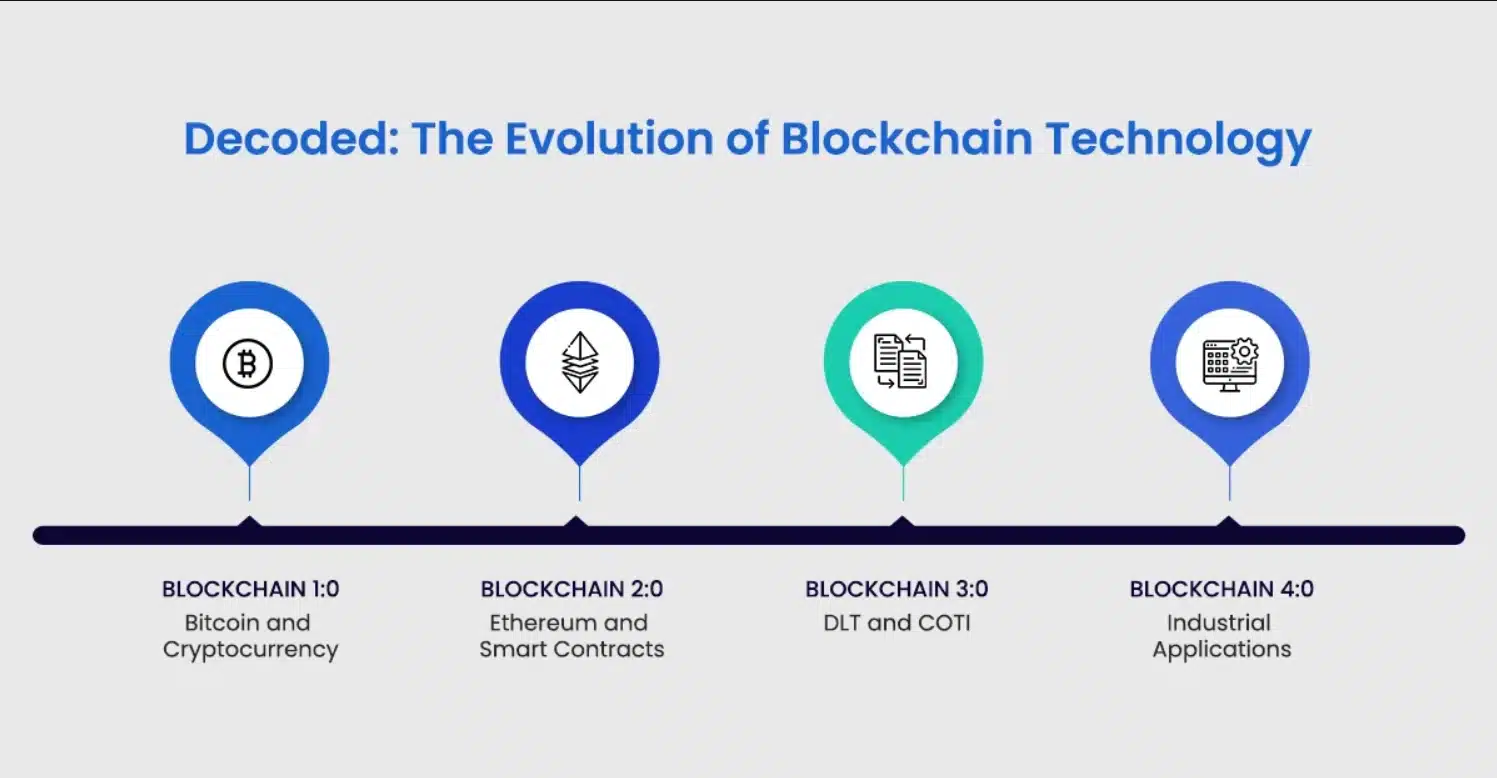
Blockchain technology has evolved through different stages with the emergence of various applications, including Currency, Smart Contracts, Decentralized Applications, and Industry.
Blockchain Technology 1.0 – Currency:
This is the first version of blockchain technology. By applying distributed ledger technology, transactions on the blockchain are processed quickly and transparently. A typical example of Blockchain 1.0 is Bitcoin, the world’s first cryptocurrency, laying the foundation for the development of the cryptocurrency market.
Blockchain Technology 2.0 – Smart Contracts:
This is the second version of blockchain technology. With smart contracts, transactions on the blockchain are significantly reduced in terms of verification costs, fraud prevention, and operation, while increasing transparency. This version completely eliminates the emotional or ethical factors commonly encountered when dealing with humans, with Ethereum being a typical example.
Blockchain Technology 3.0 – Decentralized Applications:
Decentralized Applications (dApps) are independently deployed software, not hosted on a single server but stored in a distributed manner on decentralized storage repositories and can be written in any language. Most dApp source code runs on peer-to-peer networks, in contrast to traditional applications that run on a single centralized system.
Blockchain Technology 4.0 – Industry:
Blockchain 4.0 focuses on integrating blockchain technology into industries such as finance, healthcare, logistics, and supply chain management. Companies use blockchain to enhance their products, improve services, and reduce costs.
Blockchain technology has potential applications in various fields such as Finance, Healthcare, Government, Supply Chain, Education, Real Estate, Media, Insurance, Energy, and Gaming.
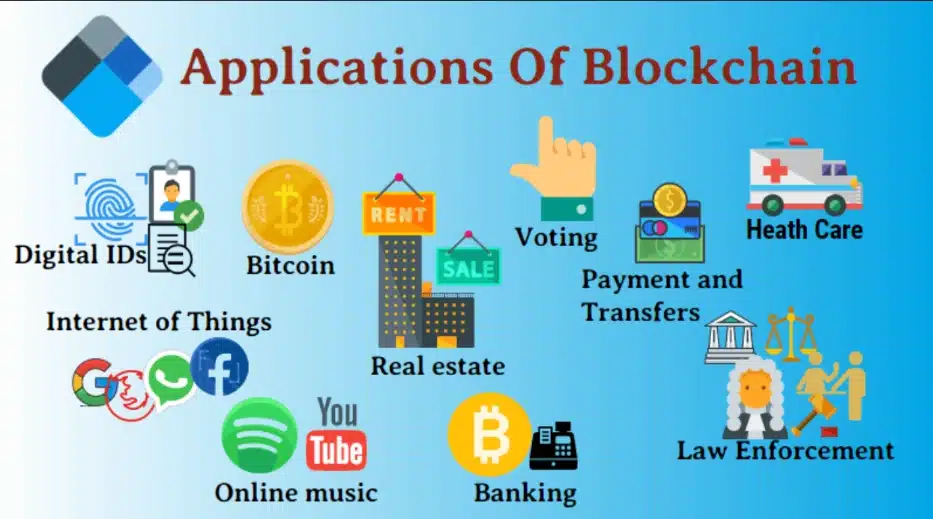
Applications of Blockchain
Some typical applications of blockchain technology include:
- Cryptocurrency: It is the first and most popular application of blockchain technology. Cryptocurrency transactions are conducted on the blockchain to ensure transparency, security, and speed.
- Smart Contracts: Created based on blockchain technology to ensure automatic execution of terms and rules written in smart contracts when preconditions are met. No one can prevent or cancel smart contracts.
- Supply Chain Management Systems: Blockchain helps enhance transparency and facilitate traceability of product origins in supply chains.
- Digital Identity: Blockchain technology helps establish a secure and tamper-proof authentication system, ensuring the security of users’ personal information.
- Real Estate: Blockchain simplifies the process of buying and selling real estate, reducing transaction fees and time.
- Copyrights: Utilizing blockchain to protect intellectual property rights, ensuring that information recorded on the blockchain cannot be altered.
- Banking and Financial Transactions: Blockchain reduces fees, time, and increases efficiency in financial transactions.
Conclusion
The article “What is Blockchain? How Does Blockchain Work?” provides a comprehensive overview of blockchain technology, its operation, features, structure, consensus mechanisms, development history, challenges, and future prospects. It aims to enhance understanding of blockchain and its applications across various industries.
If you have any further questions or would like to share your knowledge about blockchain technology, please feel free to leave a comment below. We will endeavor to respond to your inquiries as promptly as possible.










Thank you very much for the importation.
From Baze University Nigeria.
@Proffessional_Diploma_in_Bolckchain_technology
Knowledge is power
Knowledge is power,thanks for this educative article
牛逼牛逼牛逼牛逼
Nous sommes fiers d’être formé par AZCOINER Merci beaucoup
Very lucrative news feed.everything is in place in the crypto world
This is enlightening. Thanks for sharing this great knowledge.
Thanks for the information
This is an eye opener,I’m very impressed to have broad knowledge about Blockchain and it activi
Très intéressant
Thanks you so much I’m very happy to be a member of AZC before now I have not graspable the blockchain but I have know how blockchain works