What is a Dapp?
DApp, short for Decentralized Application, is a decentralized application built on blockchain technology and smart contracts.
Developed directly on blockchain platforms, the nature of DApps depends on the blockchain platform they run on. Factors such as transaction speed, TPS (transactions per second), scalability, and stability play a significant role.
Although defining DApp in a broad and simple manner may not be easy, identifying an application as a DApp can be based on several criteria:
- Open-source: The application’s source code is publicly available and accessible to everyone.
- Decentralization: It uses encryption technology similar to blockchain.
- Incentive: DApps may use virtual currency or digital assets to self-fuel their operations.
- Algorithm/Protocol: It utilizes tokens and incorporates a consensus mechanism.
Therefore, any application that meets these criteria can be considered a decentralized application.
How do DApps work?
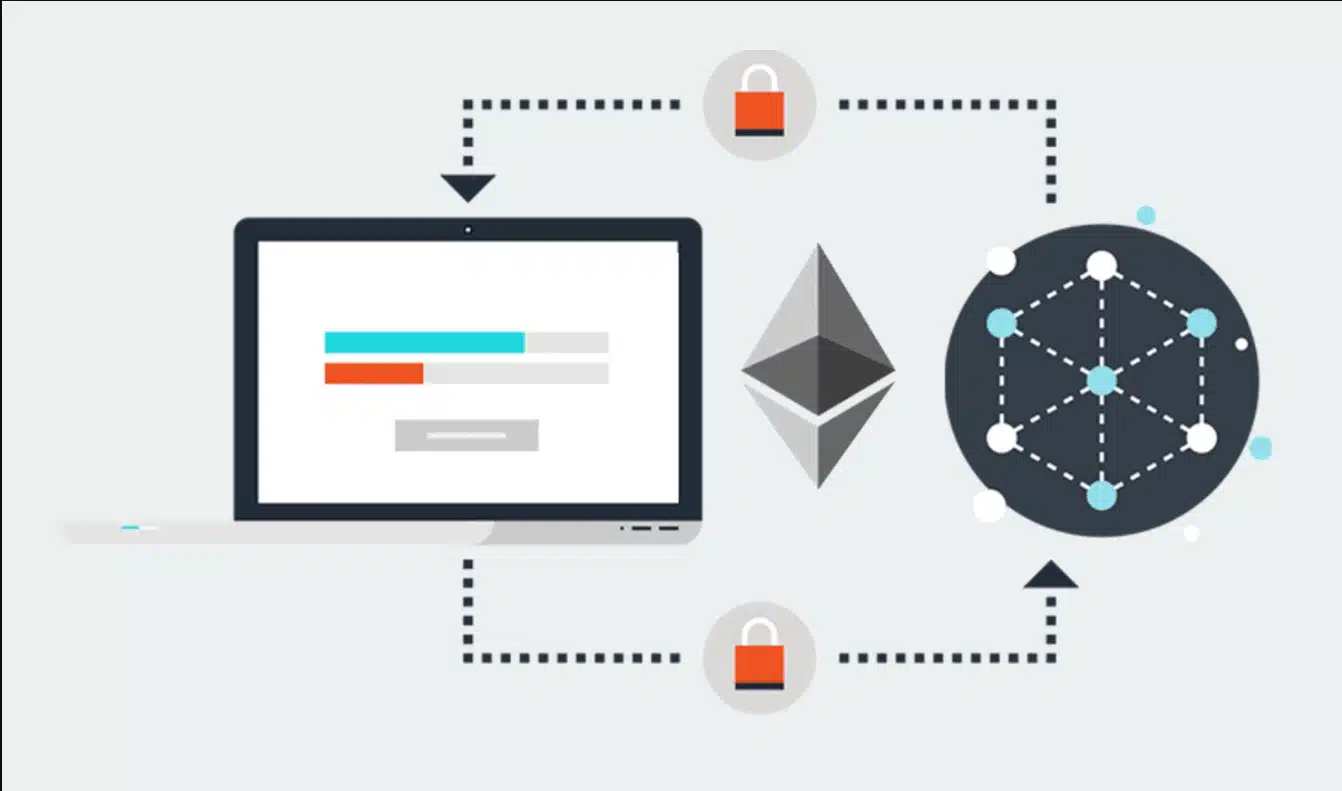
DApps operate based on source code running on a decentralized network of computers, using a consensus mechanism such as proof of work. This allows multiple computer nodes to collaborate to achieve common results, rather than relying on a single central server. The data, records, and activity logs of DApps are stored in a decentralized manner on the blockchain, ensuring transparency and security.
DApps provide user interfaces and experiences similar to traditional web and mobile applications, but their backend operates in a decentralized manner, sharing control and authority across the network.
Advantages and disadvantages of DApps

After understanding DApps, it’s essential to recognize their advantages and disadvantages in today’s digital technology.
Advantages
- Censorship resistance: DApps exist in a decentralized manner, making it challenging for governments or individuals to control the network. This creates a more free and transparent environment for users.
- No downtime: The peer-to-peer system ensures that DApps continue to operate even if individual computers or components experience network failures. This increases stability and reliability.
- Open-source: Open-source development encourages widespread development of the DApp ecosystem, allowing developers to build and improve applications flexibly and creatively.
Disadvantages
- Security risks: DApps can be hacked due to their reliance on smart contracts. Hackers can exploit vulnerabilities through these smart contracts and attack the network.
- Poor user interface: Some DApps have user interfaces that are difficult to use, which can reduce user experience and the attractiveness of the application.
- User dependency: The performance of a DApp depends on the number of users. If DApps fail to attract enough users, they will operate less efficiently and be less valuable.
Classification of DApps

Currently, there are two main classification methods based on usage purposes and blockchain technology.
Based on usage purposes:
- Decentralized exchanges
- Wallets
- Gambling applications
- Games
- Financial applications
- Social networks
- Others (including charitable organizations, healthcare, etc.)
Based on blockchain technology:
- Type I: DApps that operate on their own blockchain, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum.
- Type II: These include protocols operating on the blockchain of Type I. These protocols have tokens necessary for their functions.
- Type III: These protocols operate by using the protocols of Type II. Like Type II, Type III also has tokens necessary for their functions.
Related: What is Blockchain? How does Blockchain Work?
Applications of DApps

Although DApps are still in the early stages of development, some of them have attracted significant attention and usage.
Here are some examples:
- Decentralized exchanges: Platforms like Uniswap and PancakeSwap allow users to exchange cryptocurrencies directly without the intervention of a central intermediary.
- NFT markets: OpenSea and Rarible provide a way to create and trade non-fungible tokens, helping to build a new digital economy.
- Prediction markets: Using crowd wisdom to predict events without revealing users’ identities.
- DeFi lending applications: Platforms like Aave allow borrowing and lending of cryptocurrencies with interest rates determined by algorithms.
- Blockchain gaming applications: These apps combine ownership of NFT characters with gaming mechanics and opportunities to earn money.
Can you make money with decentralized applications?
Therefore, decentralized applications are described quite broadly and abstractly. So, how can you make money with them? Here are some ways to earn money through DApps that you can consider:
- Earn money from DApp projects on freelance platforms: You can participate in open-source development, create new DApps, and even provide other related development and deployment services.
- Participate in lending or staking DApps: You can earn money through lending or staking various cryptocurrencies on DeFi platforms. Participants will receive interest or rewards depending on their activities on the platform.
- Engage in prediction markets: You can participate in decentralized prediction platforms such as Gnosis Olympia, Augur, etc., by making accurate predictions. If your prediction is correct, you will receive an attractive reward.
The future of DApps

Although they have emerged only in recent years, it’s undeniable that DApps have a diverse range of applications.
While there are still many limitations and challenges, we can trust in a future where DApps will continue to develop strongly. Overall, the number of DApps will continue to increase based on their own benefits.
With Smart Contracts, users can create DApps to serve their own needs or, more broadly, to serve the community, thereby potentially bringing significant profits.
Conclusion
Through the article “What is a DApp? How does it work, classify and DApp applications,” have you understood about DApps yet? If not, leave a comment below to get your questions answered!








Merci pour votre explication enrichissante sur les dapp
What are smart contracts
Mohon untuk di pandu
Nice article, useful information